1. When butan-1-ol, A, is oxidized using PCC under rigorously anhydrous conditions, an aldehyde, B, is easily obtained as the product. However, if water is present during the oxidation, a carboxylic acid, C, is produced instead. When butan-2- ol, D, is oxidized with PCC, a ketone, E, is produced, regardless of whether or not water is present. Finally, 2- methylbutan-2-ol, F, cannot be oxidized using PCC under any conditions. () Explain why water affects the oxidation of a primary alcohol using PCC but net affect the oxidation of a secondary alcohol. Then, () explain why a tertiary alcohol cannot be oxidized using PCC regardless of conditions. You do not need to show any mechanisms, but be sure to draw the structures of any important intermediates discussed in your answer. :ÖH A D.
1. When butan-1-ol, A, is oxidized using PCC under rigorously anhydrous conditions, an aldehyde, B, is easily obtained as the product. However, if water is present during the oxidation, a carboxylic acid, C, is produced instead. When butan-2- ol, D, is oxidized with PCC, a ketone, E, is produced, regardless of whether or not water is present. Finally, 2- methylbutan-2-ol, F, cannot be oxidized using PCC under any conditions. () Explain why water affects the oxidation of a primary alcohol using PCC but net affect the oxidation of a secondary alcohol. Then, () explain why a tertiary alcohol cannot be oxidized using PCC regardless of conditions. You do not need to show any mechanisms, but be sure to draw the structures of any important intermediates discussed in your answer. :ÖH A D.
Chapter10: Organohalides
Section10.SE: Something Extra
Problem 19MP: The formation of Br2 from NBS first involves the reaction of NBS with HBr to form an iminol...
Related questions
Question
Using this following questions? why does water affect the oxidation of a primary alcohol but not the secondary alcohol?
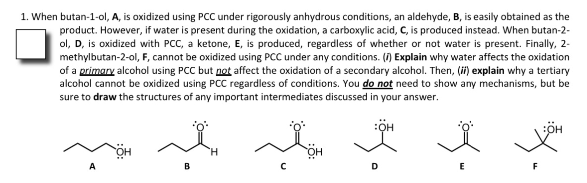
Transcribed Image Text:1. When butan-1-ol, A, is oxidized using PCC under rigorously anhydrous conditions, an aldehyde, B, is easily obtained as the
product. However, if water is present during the oxidation, a carboxylic acid, C, is produced instead. When butan-2-
ol, D, is oxidized with PCC, a ketone, E, is produced, regardless of whether or not water is present. Finally, 2-
methylbutan-2-ol, F, cannot be oxidized using PCC under any conditions. () Explain why water affects the oxidation
of a primary alcohol using PCC but not affect the oxidation of a secondary alcohol. Then, (ii) explain why a tertiary
alcohol cannot be oxidized using PCC regardless of conditions. You do not need to show any mechanisms, but be
sure to draw the structures of any important intermediates discussed in your answer.
A
B
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you


Organic Chemistry: A Guided Inquiry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9780618974122
Author:
Andrei Straumanis
Publisher:
Cengage Learning


Organic Chemistry: A Guided Inquiry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9780618974122
Author:
Andrei Straumanis
Publisher:
Cengage Learning