A beam resting on two pivots has a length of L = 6.00 m and mass M = 87.0 kg. The pivot under the left end exerts a normal force n₁ on the beam, and the second pivot placed a distance = 4.00 m from the left end exerts a normal force n₂. A woman of mass m = 52.0 kg steps onto the left end of the beam and begins walking to the right as in the figure below. The goal is to find the woman's position when the beam begins to tip. -L m M (a) Sketch a free-body diagram, labeling the gravitational and normal forces acting on the beam and placing the woman x meters to the right of the first pivot, which is the origin. (Submit a file with a maximum size of 1 MB.) Choose File No file chosen (b) Where is the woman when the normal force n₁ is the greatest? x = L m (c) What is n, when the beam is about to tip? N (d) Use the force equation of equilibrium to find the value of n₂ when the beam is about to tip. N (e) Using the result of part (c) and the torque equilibrium equation, with torques computed around the second pivot point, find the woman's position when the beam is about to tip. x = m (f) Check the answer to part (e) by computing torques around the first pivot point. x = m Except for possible slight differences due to rounding, is the answer the same? ○ Yes No
A beam resting on two pivots has a length of L = 6.00 m and mass M = 87.0 kg. The pivot under the left end exerts a normal force n₁ on the beam, and the second pivot placed a distance = 4.00 m from the left end exerts a normal force n₂. A woman of mass m = 52.0 kg steps onto the left end of the beam and begins walking to the right as in the figure below. The goal is to find the woman's position when the beam begins to tip. -L m M (a) Sketch a free-body diagram, labeling the gravitational and normal forces acting on the beam and placing the woman x meters to the right of the first pivot, which is the origin. (Submit a file with a maximum size of 1 MB.) Choose File No file chosen (b) Where is the woman when the normal force n₁ is the greatest? x = L m (c) What is n, when the beam is about to tip? N (d) Use the force equation of equilibrium to find the value of n₂ when the beam is about to tip. N (e) Using the result of part (c) and the torque equilibrium equation, with torques computed around the second pivot point, find the woman's position when the beam is about to tip. x = m (f) Check the answer to part (e) by computing torques around the first pivot point. x = m Except for possible slight differences due to rounding, is the answer the same? ○ Yes No
Related questions
Question
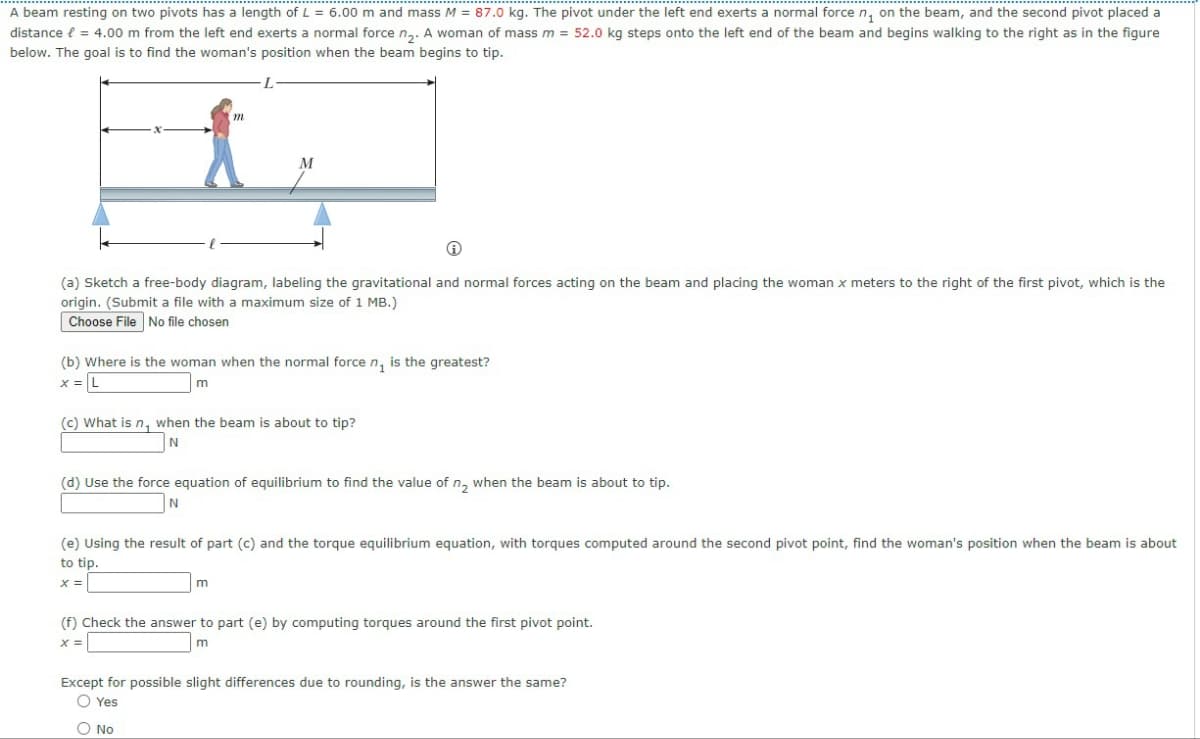
Transcribed Image Text:A beam resting on two pivots has a length of L = 6.00 m and mass M = 87.0 kg. The pivot under the left end exerts a normal force n₁ on the beam, and the second pivot placed a
distance = 4.00 m from the left end exerts a normal force n₂. A woman of mass m = 52.0 kg steps onto the left end of the beam and begins walking to the right as in the figure
below. The goal is to find the woman's position when the beam begins to tip.
-L-
m
M
(a) Sketch a free-body diagram, labeling the gravitational and normal forces acting on the beam and placing the woman x meters to the right of the first pivot, which is the
origin. (Submit a file with a maximum size of 1 MB.)
Choose File No file chosen
(b) Where is the woman when the normal force n₁ is the greatest?
x = L
m
(c) What is n, when the beam is about to tip?
N
(d) Use the force equation of equilibrium to find the value of n₂ when the beam is about to tip.
N
(e) Using the result of part (c) and the torque equilibrium equation, with torques computed around the second pivot point, find the woman's position when the beam is about
to tip.
x =
m
(f) Check the answer to part (e) by computing torques around the first pivot point.
x =
m
Except for possible slight differences due to rounding, is the answer the same?
○ Yes
No
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 6 steps with 6 images
