A dumbbell is composed of two particles, each of mass m, connected by a massless rod of length l. One particle of the dumbbell is connected by a pivot to the edge of a disk of radius r, which is massless except for a particle of mass m at its center. The disk can roll without slipping on a horizontal surface, and all motion occurs in the vertical plane of the disk. Assuming that θ and Ø are the absolute rotation angles of the disk and dumbbell, as shown, obtain the differential equations of motion. Use Lagrange Eqn.
A dumbbell is composed of two particles, each of mass m, connected by a massless rod of length l. One particle of the dumbbell is connected by a pivot to the edge of a disk of radius r, which is massless except for a particle of mass m at its center. The disk can roll without slipping on a horizontal surface, and all motion occurs in the vertical plane of the disk. Assuming that θ and Ø are the absolute rotation angles of the disk and dumbbell, as shown, obtain the differential equations of motion. Use Lagrange Eqn.
Related questions
Question
A dumbbell is composed of two particles, each of mass m, connected by a massless rod of length l. One particle of the dumbbell is connected by a pivot to the edge of a disk of radius r, which is massless except for a particle of mass m at its center. The disk can roll without slipping on a horizontal surface, and all motion occurs in the vertical plane of the disk. Assuming that θ and Ø are the absolute rotation angles of the disk and dumbbell, as shown, obtain the differential equations of motion. Use Lagrange Eqn.
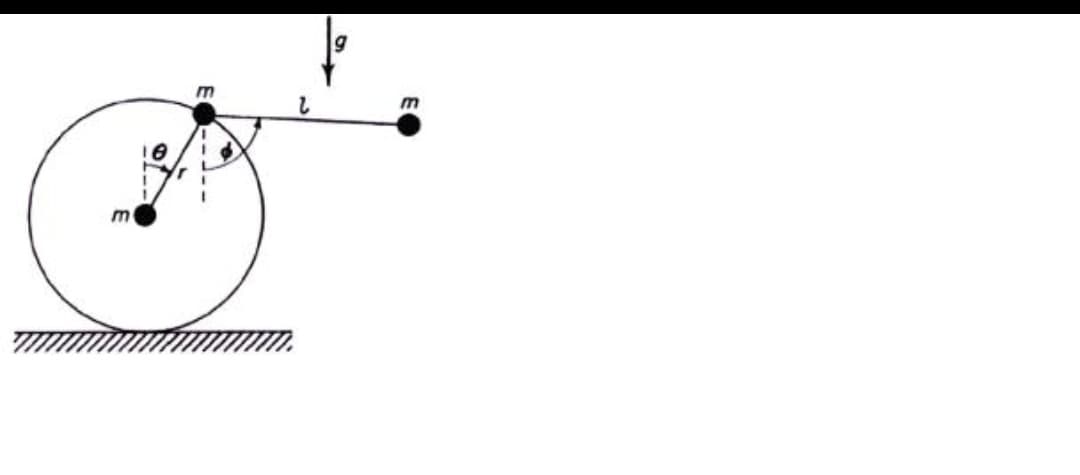
Transcribed Image Text:m
g
し
m
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 4 steps with 4 images
