PROBLEM 12 The Easy Time Grocery chain operates in major metropolitan areas on the East Coast. The stores have a "no-frills" approach, with low overhead and high volume. They generally buy their stock in volume at low prices. However, in some cases they actually buy stock at stores in other areas and ship it in. They can do this because of high prices in the cities they operate in compared with costs in other locations. One example is baby food. Easy Time purchases baby food at stores in Albany, Binghamton, Claremont, Dover, and Edison and then trucks it to six stores in and around New York City. The stores in the outlying areas know what Easy Time is up to, so they limit the number of cases of baby food Easy Time can purchase. The following table shows the profit Easy Time makes per case of baby food, based on where the chain purchases it and at which store it is sold, plus the available baby food per week at purchase locations and the shelf space available at each Easy Time store per week: Purchase Easy Time Store (profit/case) (in $) Location 3 4 5 11 12 8 6 Albany Binghamton Claremont Dover Edison Demand 1 9 10 8 4 12 25 2 8 10 6 6 10 15 6 9 8 30 5 5 9 18 7 9 7 8 6 27 6 8 7 4 10 7 35 Supply 26 40 20 40 45 Determine where Easy Time should purchase baby food and how the food should be distributed to maximize profit.
PROBLEM 12 The Easy Time Grocery chain operates in major metropolitan areas on the East Coast. The stores have a "no-frills" approach, with low overhead and high volume. They generally buy their stock in volume at low prices. However, in some cases they actually buy stock at stores in other areas and ship it in. They can do this because of high prices in the cities they operate in compared with costs in other locations. One example is baby food. Easy Time purchases baby food at stores in Albany, Binghamton, Claremont, Dover, and Edison and then trucks it to six stores in and around New York City. The stores in the outlying areas know what Easy Time is up to, so they limit the number of cases of baby food Easy Time can purchase. The following table shows the profit Easy Time makes per case of baby food, based on where the chain purchases it and at which store it is sold, plus the available baby food per week at purchase locations and the shelf space available at each Easy Time store per week: Purchase Easy Time Store (profit/case) (in $) Location 3 4 5 11 12 8 6 Albany Binghamton Claremont Dover Edison Demand 1 9 10 8 4 12 25 2 8 10 6 6 10 15 6 9 8 30 5 5 9 18 7 9 7 8 6 27 6 8 7 4 10 7 35 Supply 26 40 20 40 45 Determine where Easy Time should purchase baby food and how the food should be distributed to maximize profit.
Principles of Information Systems (MindTap Course List)
12th Edition
ISBN:9781285867168
Author:Ralph Stair, George Reynolds
Publisher:Ralph Stair, George Reynolds
Chapter2: Information Systems In Organizations
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 2CTQ2
Related questions
Question
100%
PLEASE USE EXCEL ON ANSWERING THE QUESTIONS. MAKE SURE TO TAKE A SCREENSHOT STEP BY STEP OF HOW YOU DID THE SOLUTIONS IN EXCEL. ANSWER THIS COMPLETELY TO GET AN UPVOTE. I POSTED A LOT OF THIS, IF YOU SEE THIS AGAIN, YOU CAN SEND THE SAME SOLUTIONS, I WILL STILL UPVOTE DO NOT WORRY, JUST GIVE ME THE CORRECT SOLUTIONS AND ANSWERS.
I REPEAT, ONLY EXCEL

Transcribed Image Text:PROBLEM 12
The Easy Time Grocery chain operates in major metropolitan areas on the East Coast. The stores have
a "no-frills" approach, with low overhead and high volume. They generally buy their stock in volume
at low prices. However, in some cases they actually buy stock at stores in other areas and ship it in.
They can do this because of high prices in the cities they operate in compared with costs in other
locations. One example is baby food. Easy Time purchases baby food at stores in Albany, Binghamton,
Claremont, Dover, and Edison and then trucks it to six stores in and around New York City. The stores
in the outlying areas know what Easy Time is up to, so they limit the number of cases of baby food
Easy Time can purchase. The following table shows the profit Easy Time makes per case of baby food,
based on where the chain purchases it and at which store it is sold, plus the available baby food per
week at purchase locations and the shelf space available at each Easy Time store per week:
Easy Time Store (profit/case) (in $)
4
5
7
Purchase
Location
Albany
Binghamton
Claremont
Dover
Edison
Demand
1
9
10
8
4
12
25
2
8
10
6
6
10
15
3
11
8
6
9
8
30
12
6
5
5
9
18
9
7
8
6
27
6
8
7
4
10
7
35
Supply
26
40
20
40
45
Determine where Easy Time should purchase baby food and how the food should be distributed to
maximize profit.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 1 images

Follow-up Questions
Read through expert solutions to related follow-up questions below.
Follow-up Question
PLEASE ALSO ANSWER THIS THRU EXCEL AND SHOW FORMULAS STEP BY STEP. THANK YOU I WILL UPVOTE I PROMISE.
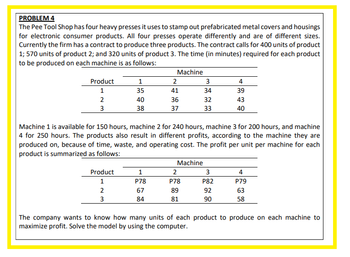
Transcribed Image Text:PROBLEM 4
The Pee Tool Shop has four heavy presses it uses to stamp out prefabricated metal covers and housings
for electronic consumer products. All four presses operate differently and are of different sizes.
Currently the firm has a contract to produce three products. The contract calls for 400 units of product
1; 570 units of product 2; and 320 units of product 3. The time (in minutes) required for each product
to be produced on each machine is as follows:
Product
1
2
3
1
35
Product
1
2
3
40
38
1
P78
Machine
67
84
2
41
36
37
Machine 1 is available for 150 hours, machine 2 for 240 hours, machine 3 for 200 hours, and machine
4 for 250 hours. The products also result in different profits, according to the machine they are
produced on, because of time, waste, and operating cost. The profit per unit per machine for each
product is summarized as follows:
Machine
3
34
32
33
2
P78
89
81
4
39
43
40
3
P82
92
90
4
P79
63
58
The company wants to know how many units of each product to produce on each machine to
maximize profit. Solve the model by using the computer.
Solution
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, computer-science and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Principles of Information Systems (MindTap Course…
Computer Science
ISBN:
9781285867168
Author:
Ralph Stair, George Reynolds
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Principles of Information Systems (MindTap Course…
Computer Science
ISBN:
9781285867168
Author:
Ralph Stair, George Reynolds
Publisher:
Cengage Learning