
8.134 and 8.135 The coefficients of friction are μS = 0.40 and μk = 0.30 between all surfaces of contact. Determine the smallest force P required to start the 30-kg block moving if cable AB (a) is attached as shown, (b) is removed.
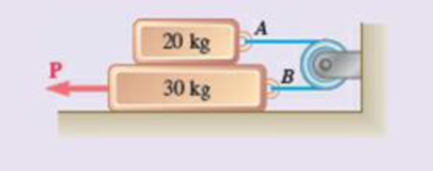
(a)
Find the smallest value of P required to start moving the 30 kg block if the cable AB is attached.
Answer to Problem 8.134RP
The smallest force P required to move the 30-kg block is
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
The coefficient of static friction is
The coefficient of kinetic friction is
Calculation:
Consider the acceleration due to gravity as
Find the weight of the 20-kg mass block as follows;
Find the weight of the 30-kg mass block as follows;
Show the free-body diagram of the 20-kg mass block as in Figure 1.
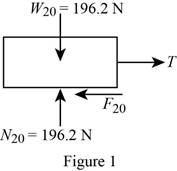
Find the normal force
Find the friction force
Substitute 0.40 for
Find the tension in the cable AB (T) by resolving the horizontal component of forces.
Show the free-body diagram of the 30-kg mass block as in Figure 2.
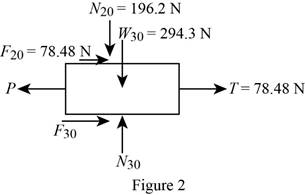
Find the normal force
Find the friction force
Substitute 0.40 for
Find the force P by resolving the horizontal component of forces.
Therefore, the smallest force P required to move the 30-kg block is
(b)
Find the smallest value of P required to start moving the 30 kg block if the cable is removed.
Answer to Problem 8.134RP
The smallest force P required to move the 30-kg block is
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
The coefficient of static friction is
The coefficient of kinetic friction is
Calculation:
Consider the acceleration due to gravity as
Find the weight of the 20-kg mass block as follows;
Find the weight of the 30-kg mass block as follows;
Show the free-body diagram of the block assembly as in Figure 3.
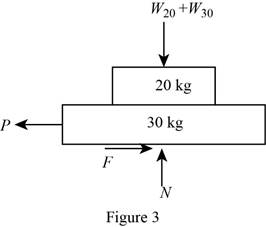
Find the normal force (N) by resolving the vertical component of forces.
Find the friction force (F) using the relation.
Substitute 0.40 for
Find the force P by resolving the horizontal component of forces.
Therefore, the smallest force P required to move the 30-kg block is
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 8 Solutions
Vector Mechanics for Engineers: Statics
- Find the largest value of b/h at which the folding table is in equilibrium. The coefficients of static friction are 0.5 at A and 0.3 at C. Neglect the weight of the table.arrow_forwardThe leather rein used to fasten the horse to the hitching rail weighs 3.5 oz per foot. The coefficient of static friction between the rail and the rein is 0.6. If a 34-lb force acting on the bridle is sufficient to restrain the horse, determine the smallest safe length L for the free end of the rein.arrow_forwardThe blocks A and B of weights WA and WB are joined by a rope that passes over the fixed peg C. The coefficients of static friction are =0.2 between block A and the inclined plane, and =0.25 between the rope and the peg. Determine the range of Wb/WA for which the system will be in equilibrium.arrow_forward
- The 60-lb plank rests on a frictionless roller at A, and the 20-lb triangular support BD. Both bodies are homogenous. The coefficients of static friction are 0.4 at B and 0.3 at D. Determine the largest force P that can be applied to the plank without initiating motion.arrow_forwardThe 40-lb spool is suspended from the hanger GA and rests against a vertical wall. The center of gravity of the spool is at G and the weight of the hanger is negligible. The wire wound around the hub of the spool is extracted by pulling its end with the force P. If the coefficient of static friction between the spool and the wall is 0.25, determine the smallest P that will extract the wire.arrow_forwardEXERCISE 2.34 The cable, whose length is 300 mm, is fastened to the 500-g block. Clockwise rotation of the arm at a constant angular speed of 5 rad/s causes the block to slide outward. The motion occurs in the vertical plane, and the coefficient of sliding friction is 0.4. Determine the tensile force in the cable and the force exerted by the block on the walls of the groove when = 53.1301⁰. 300 mm -300 mm- (Hint: use polar coordinates to solve the problem. R is from the rotation center of the arm to the block and is as shown in the Figure. Let L be the total length of the cable and S be the length from the clamped end of the cable to the end of the arm.)arrow_forward
- A 60-kg cabinet is mounted on casters that can be locked to prevent their rotation. The coefficient of static friction between the floor and each caster is 0.35. 1. If h = 600 mm, determine the magnitude of the force P (in N) required to move the cabinet to theright, if all the casters are locked. (ANSWER: 206) 2. If h = 600 mm, determine the magnitude of the force P (in N) required to move the cabinet to the right if the casters at B are locked and the casters at A are free to rotate. (ANSWER: 178)arrow_forwardProblem 3. The weightless bar AB is supported by a rope that passes over a frictionless pulley at C and a fixed peg at D. If the coefficient of static friction between the rope and the peg is µo = 0.3, determine the smallest distance x from the end of the bar at which a 20-N force may be placed and not cause the bar to move. D 20 N B.arrow_forward4. The coefficient of static friction between Box A with a mass of 220 kg and the inclined surface is 0.10. A rope, tied to the box, passes over a cylinder and the coefficient of static friction between the rope and the fixed cylinder is 0.05. Ifa woman pulls on the free end of the rope, determine a. the force the woman must exert on the rope to cause the box to start moving up the 45° 20 300 inclined surface. b. the minimum force the woman must exert on the rope to hold the box in equilibrium on the inclined surface.arrow_forward
- As shown, a man is leaning against the side of a cabinet with an unusual design. The cabinet's main body weighs 25 kg, while the upper rectangular portion weighs 3 kg. Assume the coefficients of friction between the cabinet and the floor are μs = 0.33 and μk = 0.28. Knowing that the force P exerted by the man's shoulder on the horizontal cabinet: 2. Determine which of the following is the CORRECT equilibrium equation obtained from the system's force diagram. A. ΣF = 0: N - 245.25 = 0B. ΣF = 0: P - μ N = 0C. ΣM = 0: 245.25(0.55) + 29.43(0.2) - N(x) - P(1.5) = 0arrow_forwardA clockwise couple M is applied to the circular cylinder as shown. Determine the value of M required to initiate motion for the conditions mg = 4.6 kg, mc - 4.7 kg, (s)B=0.46, (c=0.34, and r=0.21 m. Friction between the cylinder C and the block B is negligible. (s)c Answer: M = mc M mg (₂)B N.marrow_forwardQ4.) An 8-foot-long uniform slender rod is connected to a 20-lb. block by a cord and pulley system as shown where LAO = 6 ft. The coefficient of static friction between the block and the surface is 0.6. Determine the range of rod weights for which the system remains in equilibrium. Assume friction is negligible between the pulleys and the cord. Consider both slipping and tipping. 30° 30° 6 ft 2.5 ft/ B 2 ft 40⁰ 3.5 ftarrow_forward
 International Edition---engineering Mechanics: St...Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781305501607Author:Andrew Pytel And Jaan KiusalaasPublisher:CENGAGE L
International Edition---engineering Mechanics: St...Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781305501607Author:Andrew Pytel And Jaan KiusalaasPublisher:CENGAGE L
