
a
Interpretation:
Total annual parts and logistics cost for each supplier.
Concept Introduction:
The lot sizing rule consists of lot-for-lot, Fixed order quantity and Fixed period quantity. Out of all lot sizing rule, lot-for-lot rule results in least inventory because the order is planned and released according to net requirement of that particular week. A fixed order quantity is an inventory system in which a firm orders a fixed lot size i.e. the order quantity remains the same when ordered every time.
a
Explanation of Solution
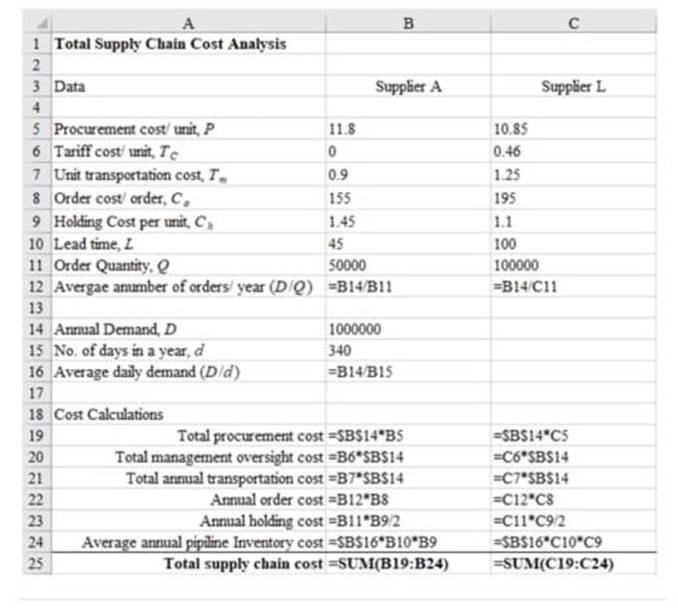
| Data | Supplier A | Supplier L |
| Procurement cost/ unit, P | $11.80 | $10.85 |
| Tariff cost/ unit, | $0.00 | $0.46 |
| Unit transportation cost, | $0.90 | $1.25 |
| Order cost/ order, | $155 | $195 |
| Holding cost per unit, | $1.45 | $1.10 |
| Lead time, L | 45 | 100 |
The different cost components that are involved in this case are:
Compute these costs for all the three suppliers and select based on the least total cost of the supply chain.
The following formulae will be used:
Total procurement cost = D.P
Total tariff cost =
Total transportation cost =
Annual ordering cost =
Annual carrying cost =
Annual pipeline inventory cost =
Where, D= annual demand, P= procurement cost per unit,
Note the computations done in the following Excel format.
| Total supply chain cost analysis | ||
| Data | Supplier A | Supplier L |
| Procurement cost/ unit, P | $11.80 | $10.85 |
| Tariff cost/ unit, | $0.00 | $0.46 |
| Unit transportation cost, | $0.90 | $1.25 |
| Order cost/ order, | $155 | $195 |
| Holding cost per unit, | $1.45 | $1.10 |
| Lead time, L | 45 | 100 |
| Order quantity | 50000 | 100000 |
| Average number of orders/ year (D/Q) | 20 | 10 |
| Annual demand, D | 1000000 | |
| No. of days in a year, d | 340 | |
| Average daily demand (D/d) | 2941 | |
| Cost calculations | ||
| Total procurement cost | $11,800,000.00 | $10,850,000.00 |
| Total management oversight cost | $0.00 | $460,000.00 |
| Total annual transportation cost | $900,000.00 | $1,250,000.00 |
| Annual order cost | $3,100 | $1,950 |
| Annual holding cost | $36,250.00 | $55,000.00 |
| Average annual pipeline Inventory cost | $191,911.76 | $323,529.41 |
| Total supply chain cost | $12,931,261.76 | $12,940,479.41 |
The following is the formulated excel sheet calculations as shown below:
b
Interpretation:
Recommendation on order quantity
Concept Introduction:
The lot sizing rule consists of lot-for-lot, Fixed order quantity and Fixed period quantity. Out of all lot sizing rule, lot-for-lot rule results in least inventory because the order is planned and released according to net requirement of that particular week. A fixed order quantity is an inventory system in which a firm orders a fixed lot size i.e. the order quantity remains the same when ordered every time.
b
Explanation of Solution
Based on the minimum total cost, the correct choice should be the Supplier A with Q = 50,000.
c
Interpretation:
Criteria for choosing supplier and quantity
Concept Introduction:
The lot sizing rule consists of lot-for-lot, Fixed order quantity and Fixed period quantity. Out of all lot sizing rule, lot-for-lot rule results in least inventory because the order is planned and released according to net requirement of that particular week. A fixed order quantity is an inventory system in which a firm orders a fixed lot size i.e. the order quantity remains the same when ordered every time.
c
Explanation of Solution
Following are some of the criteria other than then total cost. The relevant metrics for measurement are also mentioned in the following table.
| Criteria | Metric |
| Quality | Sigma level |
| Reliability | Average service level |
| Capacity | Percentage utilization |
| Delivery adherence | Variability in lead time |
d
Interpretation:
Recommendation for supplier who is not awarded the brake pad order..
Concept Introduction:
The lot sizing rule consists of lot-for-lot, Fixed order quantity and Fixed period quantity. Out of all lot sizing rule, lot-for-lot rule results in least inventory because the order is planned and released according to net requirement of that particular week. A fixed order quantity is an inventory system in which a firm orders a fixed lot size i.e. the order quantity remains the same when ordered every time.
d
Explanation of Solution
Supplier L should be given a target of reducing the procurement cost per unit by, say, 3%. Even with a 3% reduction of procurement cost per unit, it can compete with supplier A based on the total cost. This is shown below.
| Total supply chain cost analysis | ||
| Data | Supplier A | Supplier L |
| Procurement cost/ unit, P | $11.80 | $10.85 |
| Tariff cost/ unit, | $0.00 | $0.46 |
| Unit transportation cost, | $0.90 | $1.25 |
| Order cost/ order, | $155 | $195 |
| Holding cost per unit, | $1.45 | $1.10 |
| Lead time, L | 45 | 100 |
| Order quantity | 50000 | 100000 |
| Average number of orders/ year (D/Q) | 20 | 10 |
| Annual demand, D | 1000000 | |
| No. of days in a year, d | 340 | |
| Average daily demand (D/d) | 2941 | |
| Cost calculations | ||
| Total procurement cost | $11,800,000.00 | $10,524,500.00 |
| Total management oversight cost | $0.00 | $460,000.00 |
| Total annual transportation cost | $900,000.00 | $1,250,000.00 |
| Annual order cost | $3,100 | $1,950 |
| Annual holding cost | $36,250.00 | $55,000.00 |
| Average annual pipeline Inventory cost | $191,911.76 | $323,529.41 |
| Total supply chain cost | $12,931,261.76 | $12,614,979.41 |
Want to see more full solutions like this?
- “Supply chain management has been a very vital tool in the competitive world of business, and this depends on the product and its supply chain. Managing inventory is a critical activity for the success of supply chain since inventory impacts the costs of goods sold as well as supports customer service”. Discuss the validity of this statementarrow_forwardNo written by hand solution The questions below refer to the following SAME paragraph: Suppose a retailer Mojo, holds safety stock for an item to accommodate a 98% service level with uncertain demand. There are two supply options: Supplier X taking 5 days to deliver replenishments, and Supplier Y taking 3 days to replenish. Both suppliers charge the same price for the item. Ignoring differences in fixed order costs, the retailer should choose: Group of answer choices Supplier X Option Y only if the critical ratio is less than 0.9 Option X only if the critical ratio is greater than 0.9 Supplier Yarrow_forwardGiven the information provided below, what are the procurement, oversight, transportation, order cycle inventory, pipeline inventory costs, and total supply chain costs for using the supplier Ebert, Inc. Ebert manufactures small speakers for automobiles in its factory in the Philippines. The order size is Q= 7,000 units and the supply chain operates 300 days a year. Do not round intermediate calculations. Round your answers to the nearest dollar. CertifiedSupplier AnnualDemand (D) Price perUnit (P) OversightCost perUnit (O) Transport Costper Unit (Ct ) Order Cost(Co ) Cost toStore OneUnit OneYear (Ch ) Order LeadTime inDays (L) Elbert, Inc. 224,000 $6.99 $0.22 $2.38 $140 $5.39 55 Procurement cost: $ Oversight cost: $ Transportation cost: $ Order cycle cost: $ Inventory holding cost: $ Pipeline invenory cost: $ Total supply chain costs: $arrow_forward
- Describe the supply chain for your university or college.Who are the suppliers, producers, and distributors in thissupply chain? Are there different supplier tiers? Howwould you evaluate this supply chain? Does inventory evenexist, and if it does, what form does it take?arrow_forwardHorizon Cellular manufactures cell phones for exclusive use in its communication network. Management must select a circuit board supplier for a new phone soon to be introduced to the market. The annual requirements (D) are 40,000 units and Horizon's plant operates 250 days per year. The data for three suppliers are in the attached table. Annual Freight Costs Shipping Quantity (Q) Supplier 10,000 20,000 Price/Unit (p) Annual Holding Cost/Unit (H) Lead Time (L) (days) Annual Administrative Cost Material Costs Abbott $11,000 $8,500 $29 $5.80 4 $11,000 $232,000.00 Baker $12,000 $9,500 $31 $6.20 3 $12,000 $1,240,000 Carpenter $9,000 $7,000 $28 $5.60 8 $9,000 $1,120,000 Which supplier and shipping quantity will provide the lowest total cost for Horizon Cellular? Using the supplier [X] and a shipping quantity of [X] units is the lowest cost alternative, with annual total costs to Horizon Cellular of [X]. (Quantity and Annual Total Costs are integer…arrow_forwardOne of your Taiwanese suppliers has bid on a new line of molded plastic parts that is currently being assembled at your plant. The supplier has bid $0.10 per part, given a forecast you provided of 200,000 parts in year 1; 300,000 in year 2; and 500,000 in year 3. Shipping and handling of parts from the supplier’s factory is estimated at $0.01 per unit. Additional inventory handling charges should amount to $0.005 per unit. Finally, administrative costs are estimated at $20 per month. Although your plant is able to continue producing the part, the plant would need to invest in another molding machine, which would cost $10,000. Direct materials can be purchased for $0.05 per unit. Direct labor is estimated at $0.03 per unit plus a 50 percent surcharge for benefits; indirect labor is estimated at $0.011 per unit plus 50 percent benefits. Up-front engineering and design costs will amount to $30,000. Finally, management has insisted that overhead be allocated if the parts are made in-house…arrow_forward
- Supply chain management has been a very vital tool in the competitive world of business, and this depends on the product and its supply chain. Managing inventory is a critical activity for the success of supply chain since inventory impacts the costs of goods sold as well as supports customer service”. Discuss the validity of this statement Detailyarrow_forwardHow might other companies (including services) use vendormanaged inventory in its supply chain design? Discuss theadvantages and disadvantages of VMI.arrow_forwardOne of your Taiwanese suppliers has bid on a new line of molded plastic parts that is currently being assembled at your plant. The supplier has bid $0.10 per part, given a forecast you provided of 400,000 parts in one year1. 500,000 in year 2; 700,000 in year 3. shipping and handling of parts from the supplier’s factory is estimated at $0.01 per unit. Additional inventory handling charges should amount to $0.006 per unit. Finally, administrative costs are estimated at $30 per month. Although your plant can continue producing the part, the plant would need to invest in another molding machine, which would cost $20,000. Direct materials can be purchased for $0.06 per unit. Direct labor is estimated at $0.05 per unit plus a 50% surcharge for benefits and, indirect labor is estimated at $0.008 per unit plus 50% benefit. Up-front engineering and design costs will amount to $40,000. Finally, management has insisted that overhead be allocated if the parts are made in-house at a rate of 100%…arrow_forward
- Explain how are service level and inventory level dependent on each other ?arrow_forwardOne of your Taiwanese suppliers has bid on a new line of molded plastic parts that is currently being assembled at your plant. The supplier has bid $0.10 per part, given a forecast you provided of 300,000 parts in year 1; 500,000 in year 2; and 700,000 in year 3. Shipping and handling of parts from the supplier's factory is estimated at $0.03 per unit. Additional inventory handling charges should amount to $0.004 per unit. Finally, administrative costs are estimated at $20 per month. Although your plant is able to continue producing the part, the plant would need to invest in another molding machine, which would cost $10,000. Direct materials can be purchased for $0.04 per unit. Direct labor is estimated at $0.05 per unit for wages plus a 50 percent surcharge for benefits and, indirect labor is estimated at $0.013 per unit plus 50 percent benefits. Up-front engineering and design costs will amount to $40,000. Finally, management has insisted that overhead be allocated if the parts are…arrow_forwardDoes the supplier have bar coding capability or radio frequency identification (RFID) technology?arrow_forward
 Purchasing and Supply Chain ManagementOperations ManagementISBN:9781285869681Author:Robert M. Monczka, Robert B. Handfield, Larry C. Giunipero, James L. PattersonPublisher:Cengage Learning
Purchasing and Supply Chain ManagementOperations ManagementISBN:9781285869681Author:Robert M. Monczka, Robert B. Handfield, Larry C. Giunipero, James L. PattersonPublisher:Cengage Learning
