
(a)
The natural rate of
(a)
Explanation of Solution
The IS LM framework of the economy deals with the closed economy and does not consider the international trade and Balance of Payments into consideration. This leads to the generation of the new model that incorporated the Balance of Payment into the calculations which is known as the Mundell - Fleming model. The
The natural rate of unemployment is the unemployment rate in the economy at the time when the labor market is in equilibrium. Thus, it consists of the structural and frictional unemployment in the economy when the economy is operating efficiently. This natural rate of unemployment is a case where the inflation in the economy will be equivalent to the expected rate of inflation. Thus, there will be no deviation to the actual level of inflation from the expected.
Thus, the expected inflation in this case will be equal to the last period's inflation in the economy. Thus, setting the inflation to the last period's inflation,
Natural Rate of Unemployment: The natural rate of unemployment is the rate of unemployment that is persisting in the economy when the labor market of the economy is in its equilibrium.
(b)
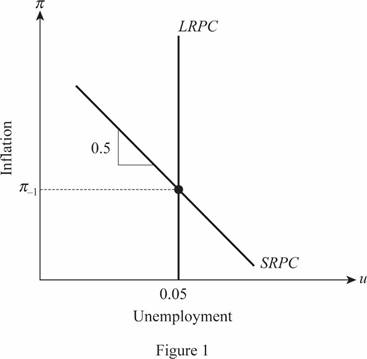
The short run and long run relationship between the inflation and unemployment.
(b)
Explanation of Solution
The inflation and the unemployment are the two important aspects that an economy has to handle very carefully. When the measure to tackle and reduce the inflation is taken, it will increase the unemployment and vice versa in the economy. This happens in the short run and thus, they both are inversely related with each other. This short run or single period relation between the inflation and the unemployment is explained using the Phillips curve for the economy. Here, the expected inflation rate is equal to the last period's inflation rate and the slope of the Phillips curve will be 0.5. The short run Phillips curve will pass through the point where the
The long run period or the multi period relation is different from the short run relation. The expected inflation of the economy will be equal to the actual level of inflation in the economy. Thus,
(c)
The cyclical unemployment required to reduce the inflation by 4 percentage points.
(c)
Explanation of Solution
The Phillips curve of the economy is given to be
When the inflation has to be reduced, the unemployment in the economy should be above its natural level of unemployment according to the Phillips curve. Thus, the required fall in the inflation rate should be plugged into the left side of the Phillips curve equation as follows:
Thus, it indicates that there should be 8 percent more cyclical unemployment in the economy in order to bring the inflation by 4 percentage. The Okun's law states that an increase in the unemployment by 1 percent will correspond to the 2 percent fall in the total
The sacrifice ratio is the ratio of the percentage of GDP that the economy must foregoin order to reduce the inflation by 1 percentage point. Here, the total GDP foregone is 16 percentage points and the total inflation reduced is 4 percentage points. Thus, the sacrifice ratio can be calculated by dividing the total GDP foregone with the inflation reduced as follows:
Thus, the sacrifice ratio of the economy is 4.
(d)
The scenarios to reduce the inflation by 4 percentage points.
(d)
Explanation of Solution
The Phillips curve of the economy is given to be
In order to reduce the inflation by 4 percentage points, the economy should have to face the higher unemployment rate of 13 percent for the short run as calculated above. Thus, the first measure that the government can relay is to make the unemployment rate very high at 13 percent in order to reduce the inflation by 4 percentage points.
The second measure that the government can relay is to fix the level of unemployment at 7 percent for 4 years which would slowly reduce the level of inflation in the economy by 4 percentage points. These are the two different measures that the government can relay up on in order to reduce the inflation by 4 percentage points.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
- If the inflation rate is positive, the price level in an economy is Select one: A. falling slowly. B. falling rapidly. C. constant. D. zero. E. rising.arrow_forward1) Whether you gain or lose during a period of inflation depends on: a) how the price increases affect government purchases of goods. b) whether the economy is expanding or contracting. c) whether you save or not. d) whether your income rises faster or slower than prices of the things you buy. 2) A real wage that does not keep pace with inflation implies: a) a decrease in purchasing power. b) a decrease in nominal wages. c) a decrease in nominal wages after inflation. d) an increase in the inflation adjusted real wage.arrow_forwarda. Suppose that the economy is at an inflation rate such that unemployment is above the natural rate. How does the economy return to the natural rate of unemployment? b. Suppose the central bank wants to permanently reduce the inflation rate. What are the possible ways of doing so? c. What information does the sacrifice ratio tell us about the consequences of reducing inflation? B v E v + v Pa... ... IIIarrow_forward
- which of the following is true Select one: a. When the actual rate of unemployment is low than natural rate, the inflation rate decreases b. natural rate of unemployment is that rate of unemployment required to keep the inflation rate constant c. When the actual rate of unemployment is higher than natural rate, the inflation rate increases d. the natural rate can never be the non-accelerating inflation rate of unemploymentarrow_forwardSuppose πt = πt−1 −2(ut −0.04) is the Phillips Curve equation in the economy. Answer thefollowing questions.a. What is the natural rate of unemployment?b. Graph the short run and the long run relationship between inflation and unemployment.c. How much cyclical unemployment is necessary to reduce inflation by 10 percentagepoint?d. The inflation is running at 12 percent. The Central Bank wants to reduce it to 9 percent.Give two scenarios that will achieve the goal.arrow_forwardIn theory, inflation not only ______ the value of consumers' money over time, but it also increases the ____ of producers over time. a.Decreases, wages b.Increases, interest rates c.Decreases, unemployment d.Increases, real GDParrow_forward
- Suppose short-run output exceeds full potential output by 3 percent. a. According to Okun's law, what is the effect on unemployment? b. Assuming that inflationary expectations are constant, what is the effect on wages?arrow_forwardThe Phillips curve is A. a positive relationship between price stability and constant, small-increment changes in the fiscal policy on the part of the Fed. B. a positive relationship in the long run between the rate of inflation and the rate of unemployment. C. a negative relationship between the inflation rate and the unemployment rate, at least in the short run. D. a positive relationship between the unemployment rate and the real Gross Domestic Product (GDP) level.arrow_forwardAssume that expected inflation is based on the following: n = 0+1. An increase in 8 will cause a. a reduction in the natural rate of unemployment. b. an increase in the natural rate of unemployment. c. inflation in period t to be more responsive to changes in unemployment in period t. d. None of the other answers is correct. e. no change in the natural rate of unemployment.arrow_forward
- A Phillip's curve is given by π = n + 10% - 2u, where = π-1 and also Tt-1 = 2%. Calculate the natural rate of unemployment. Imagine further that the economy at time t is at the natural rate of unemployment. Calculate the inflation rate at time t. Imagine further that the unemployment rate at time t+1 is 1 percentage point lower then at time t. Calculate the inflation rate at time t+1.arrow_forwardInflation and unemployment data for Acadia can be found in the table below. Year 2018 2019 2020 ion Rate (%) 5 Inflation Rate (%) + 4.7 2.6 3.5 a. Draw a graph showing the Phillips curve for Acadia based on the values for inflation and unemployment in this economy from 2018 to 2020. Plot 3 points in total to draw the Phillips curve for Acadia below. Plot the plotting points in the order 2018, 2020 and then 2019. Unemployment Rate (%) Phillips Curve for Acadia 5.7 8.9 6.8 Tools Phillips Curve Ⓡarrow_forwardSuppose that an economy has the Phillips curvep=p-1 - O.S(u - 0.06),a) What is the natural rate of unemployment?b) Graph the short-run and long-run relationships between inflation and unemployment.c) How much cyclical unemployment is necessary to reduce inflation by S percentage points?d) Using Okun's law, compute the sacrifice ratio e.e)Inflation is running at 10 percent. The Fed wants to reduce it to 5 percent. Give Iwoscenarios that will achieve that goal.arrow_forward
 Exploring EconomicsEconomicsISBN:9781544336329Author:Robert L. SextonPublisher:SAGE Publications, Inc
Exploring EconomicsEconomicsISBN:9781544336329Author:Robert L. SextonPublisher:SAGE Publications, Inc
