
Concept explainers
Interpretation:
Molecular geometry and electron geometry about each non-hydrogen atom in the given molecule is to be predicted using VSEPR theory.
Concept introduction:
Electron geometry and molecular geometry of molecules are determined by using Valence shell electron pair repulsion (VSEPR) theory. According to VSEPR theory, electron geometry describes the orientation of the electron groups about a particular atom and molecular geometry describes the arrangement of atoms about a particular atom.
The number of electron pairs describes the electron and molecular geometry. If all the electron pairs are bonds, then the molecular geometry is the same as the electron geometry. Electron geometry is different from molecular geometry if some electron groups are present as lone pairs. The bond angle depends on the electron geometry around the atom.
Electron geometry and molecular geometry from the number of electron pairs and bond angle according to VSEPR theory are as follows:
| Number of Electron Groups |
Number of Bonds |
Number of Lone Pairs |
Bond Angle (o) |
Electron Geometry | Molecular Geometry |
| 2 | 2 | 0 | 180 | Linear | Linear |
| 3 | 3 | 0 | 120 | Trigonal planar | Trigonal planer |
| 3 | 2 | 1 | 120 | Trigonal planar | Bent |
| 4 | 4 | 0 | 109.5 | Tetrahedral | Tetrahedral |
| 4 | 4 | 0 | 180 | Linear | Linear |
| 4 | 2 | 2 | 109.5 | Tetrahedral | Bent |
Answer to Problem 2.2P
According to VSEPR theory, the electron and molecular geometry about each of the non-hydrogen atom in the structure is as follows:
Oxygen = Electron geometry is tetrahedral while molecular geometry is bent.
C1 carbon atom = Electron geometry is tetrahedral while molecular geometry is also tetrahedral.
C2 and C3 carbon atoms = Electron geometry is linear while molecular geometry is also linear.
Explanation of Solution
The given structure for
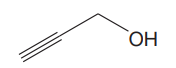
The structure showing all the atoms and lone pairs is:
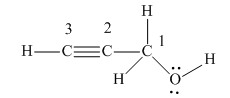
There are four non-hydrogen atoms in the above structure. They are numbered from 1 to 4.
There are four groups of electrons around the oxygen atom: two lone pairs of electrons and two single bonds. According to VSEPR theory, its electron geometry is tetrahedral, and its molecular geometry is bent.
There are four groups of electrons around the C1 carbon: four single bonds and no lone pairs of electrons. According to VSEPR theory, its electron geometry is tetrahedral, and its molecular geometry is also tetrahedral.
There are two groups of electrons around the C2 carbon: one triple bond, and one single bond, and no lone pairs of electrons. According to VSEPR theory, its electron geometry is linear, and its molecular geometry is also linear.
There are two groups of electrons around the C3 carbon: one triple bond, one single bond, and no lone pairs of electrons. According to VSEPR theory, its electron geometry is linear, and its molecular geometry is also linear.
The electron geometry and molecular geometry about each non-hydrogen atom in the given molecule is predicted on the basis of VSEPR chart.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 2 Solutions
Organic Chemistry: Principles and Mechanisms (Second Edition)
- I’m not sure how to draw this where there would only be one chiral carbon AND be branchedarrow_forwardProblem (1) Which of the following compounds show cis-trans isomerism? Draw the cis and trans isomers of those that do. CHF=CHF FC CH2 CH;=CH-CH,-CH3 -CHCH, -CHCHCH, CHCH,arrow_forwardWhich of the following is a chiral molecule/s?arrow_forward
- Part A Alkanes are molecules that contain only carbon and hydrogen and have only single bonds. Straight-chain What is the molecular formula for the alkane shown in the model? alkanes have all the carbon atoms connected in a Express your answer as a chemical formula. row, branched-chain alkanes have branching connections of carbon atoms, and cycloalkanes contain rings of carbon atoms. • View Available Hint(s) ? CH, CH, DA chemical reaction does not occur for this question. Submit Previous Answers X Incorrect; Try Again; 5 attempts remaining Figure View Available Hint(s) Pentanearrow_forwardQuestion 12 of 30 What is the expected product from the addition reaction of 1-pentene (CH₂=CHCH₂CH₂CH₂) with bromine (Br₂)? A) 1,2-dibromopentane B) 1-bromopentane C) 1-bromopentene D) 2-bromopentane E) 1,2-bromopentenearrow_forwardFatty acids are molecules with a carboxylic acid on one end and long hydrocarbon chain on the other. The sodium salts of fatty acids (such as sodium strearate, shown below) are commonly used in soaps to trap nonpolar dirt and grease particles. Soap does not work well in "hard water, which is water with high concentration of magensium and calcium ions (often found in water obtained from wells) Explain this observation at a molecular level.arrow_forward
- Hw problem wants 2 structures that have the same molecular formula but different connectivities for C3H4arrow_forwardA) classify the compounds below as alkanes, alkenes, aligned, alcohols (primary, secondary or tertiary), carboxylic acids, esters and amides (primary, secondary or tertiary). If no compound of a particular class is present answer n/a. B) identify all isomers of compounds 1a, 1b, 1c, 1d and 1e. C) Sort compounds 1a, 1b, 1d, 1e, 1f, 1h, 1k, 1n and 1m in order of increasing boiling point. D) Sort compounds 1o, 1h and 1l in order of increasing solubility in water and briefly explain why.arrow_forwardQuestion:What is the significance of the LUMO (Lowest Unoccupied Molecular Orbital) in organic chemistry, and how does it contribute to chemical reactions?arrow_forward
- Draw molecule and write IUPAC. (Could be line or condensed structure)arrow_forwardMatch the type of strain to the definition: Torsional strain: a) strain caused by interactions of 2 groups/ electron Clouds through space b) strain caused by the rotation of siqma bonds 2) strain caused when a structure has deviations from ideal bond angles D d) strain caused by interactions of 2 groups that causing causes forsion / twistingarrow_forward) Draw the resonance forms of benzene, cyclobutadiene, and cyclooctatetraene, showingall the carbon and hydrogen atoms.arrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





