
Tutorials in Introductory Physics
1st Edition
ISBN: 9780130970695
Author: Peter S. Shaffer, Lillian C. McDermott
Publisher: Addison Wesley
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Textbook Question
Chapter 27.2, Problem 2dTH
One mole of an ideal gas is confined to a container with a movable piston. The questions below refer to the processes shown on the PV diagram at right. Process I is a change front state X to state Y at constant pressure. Process II is a change from state W to state Z at a different constant pressure.
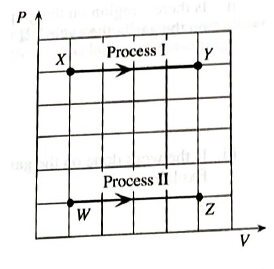
d. In Process I, is the
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
Shown below are bar charts for processes
involving ideal gasses. For each, draw the
appropriate line or curve on the PV graph,
including an arrow for direction. Explain.
1.
Temperature Pressure Volume
bul
IF IF I F
2.
Temperature Pressure Volume
T
I FI FI F
4.
I F
IF I F
P
Temperature Pressure Volume
7 G
I FI FI F
P
3. For this, use the ideal gas law as a guide:
Temperature Pressure Volume
P
V
P
V
V
Suppose a monatomic ideal gas is changed from state A to state D by one of the processes shown on the PV diagram.
1. The gas follows the constant-temperature path AC followed by the constant-pressure path CD.
What is the total work done on the gas ?
What is the total change in internal energy of the gas during the entire process?
What is the total heat flow into the gas?
Part B
A container holds a sample of ideal gas in thermal equilibrium, as shown in the
figure. (Figure 1) One end of the container is sealed with a piston whose head is
perfectly free to move, unless it is locked in place. The walls of the container readily
allow the transfer of energy via heat, unless the piston is insulated from its
surroundings.
Starting from equilibrium at point 0, what point on the pV diagram will describe the ideal gas after the following process?
"Immerse the container into a large water bath at the same temperature, and very slowly push the piston head further into the container."
• View Available Hint(s)
O point 1
O point 2
O point 3
O point 4
O point 5
O point 6
O point 7
O point 8
Submit
Previous Answers
X Incorrect; Try Again; 4 attempts remaining
The volume of the gas cannot remain constant because the piston head has moved further into the container.
Part C
Starting from equilibrium at point 0, what point on the pV diagram will describe the ideal gas…
Chapter 27 Solutions
Tutorials in Introductory Physics
Ch. 27.1 - Prob. 1aTHCh. 27.1 - In this process, which of the quantities P, V, n,...Ch. 27.1 - Consider the following incorrect student...Ch. 27.1 - Explain why it is not possible to use the ideal...Ch. 27.1 - A long pin is used to hold the piston in place as...Ch. 27.1 - A long pin is used to hold the piston in place as...Ch. 27.1 - Prob. 2cTHCh. 27.2 - Prob. 1aTHCh. 27.2 - Prob. 1bTHCh. 27.2 - Prob. 1cTH
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Find more solutions based on key concepts
If a thermometer were placed in each of the lighted areas, which one would read the higher temperature?
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
14. A rifle is aimed horizontally at a target 50 m away. The bullet hits the target 2.0 cm below the aim point....
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: A Strategic Approach, Vol. 1 (Chs 1-21) (4th Edition)
What gas makes up most of the Martian atmosphere?
Conceptual Integrated Science
the accurate reason how private people get to decide in which federal government should finance projects.
Glencoe Physical Science 2012 Student Edition (Glencoe Science) (McGraw-Hill Education)
The frequency heard by the moth.
Physics (5th Edition)
A block 20% more massive than you hangs from a rope that goes over a frictionless, massless pulley. With what a...
Essential University Physics: Volume 1 (3rd Edition)
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- An ideal gas undergoes two thermodynamic processes as shown in FIGURE 1. a. Name the processes AB and BC. b. If the initial temperature is 40°C, find the temperatures at B and C. c. Find the total work done d. What is the total change in internal energy for these processesarrow_forward13 moles of monatomic ideal gas undergoes a thermodynamic process from point a topoint c, as shown by the PV diagram in Figure 1. i) Determine the work done ON the gas from point a to point c ii) Find the temperature of the gas at point barrow_forward13 moles of monatomic ideal gas undergoes a thermodynamic process from point a to point c, as shown by the PV diagram in Figure 1. i) Determine the work done ON the gas from point a to point c. ii) Find the temperature of the gas at point b.arrow_forward
- The gas cylinder in (Figure 1) is well insulated except for the bottom surface, which is in contact with a block of ice. The piston can slide without friction. The initial gas temperature is >0°C. Figure 1 of 1 Part Gas During Explair Ice Match iarrow_forwardProblem 2 Suppose an irreversible process takes 1.0 mol of monoatomic ideal gas from state 1 to state 2, where pressure increases linearly with volume as shown in the diagram below. P2 Suppose that the following measurements are taken: 1 P1 Pi=101,000 N/m? Vi = 0.010 m³ p2=185,000 N/m? V2 = 0.026 m V1 V2 Calculate the following: a) work done on the system for the process. b) heat into the system for the process. c) AUsys for going from state 1 to 2. Give your answer in units of joules (J). d) ASsys for going from state 1 to 2. Give your answer in units of J/K. e) What can be known about ASsurr for this process? V (m³) p (N/m²)arrow_forwardGive an equation for the infinitesimal change in entropy, ??, of a system in terms of the heat transfer ??? and the temperature ? at which the heat transfer occurs. Explain the sign convention.ii. A litre of water at 20 °C is placed in a fridge at 5 °C. Calculate the change in entropy of the water, including the sign, once all the water has come into thermal equilibrium.iii. Calculate the change in entropy of the fridge from part ii, including the sign.iv. Demonstrate that the Second Law has been obeyed in the process described in ii and iii.arrow_forward
- A gas undergoes the process shown in the diagram below. During the process AB, the internal energy of the gas decreases and a certain amount of heat Q goes out of the system for the process CA. Use this information to answer the questions below. Options for each selection is Positive, Negative, or Zero (check attached image) (a) What are the signs of W (work done by the gas), Q, and ΔU for the process CA?(b) What are the signs of W (work done by the gas), Q, and ΔU for the process AB?(c) What are the signs of W (work done by the gas), Q, and ΔU for the process BC?arrow_forwardQuestion 2 A particular power plant operates with a heat-source reservoir at 350°C and a heatsink reservoir at 30°C. It has a thermal efficiency equal to 55% of the Carnot-engine thermal efficiency for the same temperatures. What is the thermal efficiency of the plant? Use the editor to format your answerarrow_forwardpin 6. A long pin is now used to hold the piston in place as shown in the diagram. The cylinder is then placed into boiling water. The valve remains closed for the whole time. a. Does the temperature of the gas increase, decrease, or remain the same? b. Sketch this process in the PV diagram. Using arrow, indicate the direction of the process on your graph. c. Explain why for this particular situation, it is impossible to determine the pressure of the gas as you did on question 1 (that is, by considering the free-body-diagram of the piston).arrow_forward
- The pV diagram in the figure (Figure 1) shows a process abc involving 0.350 mol of an ideal gas. What was the temperature of this gas at points a, b, and c? How much heat had to be put in during the process to increase the internal energy of the gas by 1.30×104 J ?arrow_forwardPart A A cube 21 cm on each side contains 3.2 g of helium at 20°C. 1300 J of heat are transferred to this gas. What is the final pressure if the process is at constant volume? Express your answer with the appropriate units. • View Available Hint(s) µA = Value Units Submit Part B What is the final volume if the process is at constant pressure? Express your answer with the appropriate units. • View Available Hint(s) µÀ V = Value Unitsarrow_forwardIn the pV diagram shown in the figure (Figure 1), 80.0 J of work was done by 0.0610 mole of ideal gas during an adiabatic process. a) How much heat entered or left this gas from a to b? Express your answer in joules. b) By how many joules did the internal energy of the gas change? Express your answer in joules. c) What is the temperature of the gas at b? Express your answer in kelvins.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:9780133969290
Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:9781107189638
Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:9780321820464
Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...
Physics
ISBN:9780134609034
Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:PEARSON
The Laws of Thermodynamics, Entropy, and Gibbs Free Energy; Author: Professor Dave Explains;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=8N1BxHgsoOw;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY