
(a)
Interpretation:
The element that is highlighted in yellow in the periodic table is present in p area or d area has to be determined.
Concept Introduction:
Periodic law states that if the elements are arranged in increasing order of
Location of an element in a periodic table can be given by the period number and the group number. The horizontal row in a periodic table where the elements are present is known as Period. The vertical column in a periodic table where the elements are present is known as Group.
Chemical properties of the elements repeat themselves at regular intervals because of the electronic configuration. The elements that are present in a Group have similar chemical properties. This is because the outer-shell electronic configuration will be the same.
The periodic table has all the elements that can be distinguished based on the outer-shell electron. If the outer-shell electron is present in s subshell, then the elements are present in s area of periodic table. If the outer-shell electron is present in p subshell, then the elements are present in p area of periodic table. If the outer-shell electron is present in d subshell, then the elements are present in d area of periodic table. If the outer-shell electron is present in f subshell, then the elements are present in f area of periodic table.
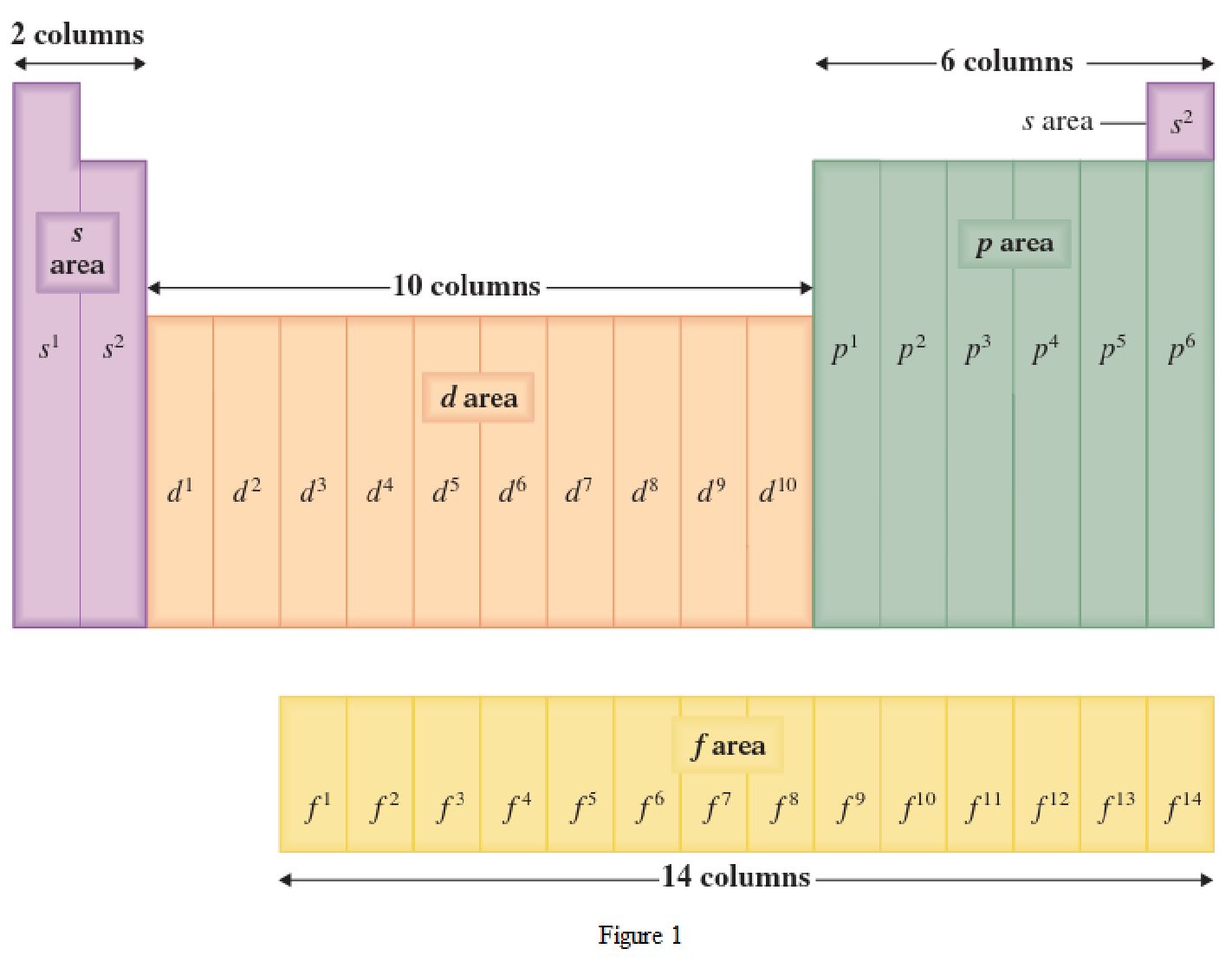
Distinguishing electron is the one that is the last electron added to the electronic configuration of an element when the electron subshells are filled in the order of increasing energy. This distinguishing electron determines the area of the element in the periodic table. This is because this only causes the element electronic configuration to differ from other elements.
(b)
Interpretation:
The element that is highlighted in blue in the periodic table is present in s area or d area has to be determined.
Concept Introduction:
Periodic law states that if the elements are arranged in increasing order of atomic number, then the elements with similar chemical properties occur at regular intervals or periodic intervals. The elements are arranged in a periodic table in which the arrangement was based on the atomic number of the elements and the elements that have similar chemical properties are positioned in vertical columns.
Location of an element in a periodic table can be given by the period number and the group number. The horizontal row in a periodic table where the elements are present is known as Period. The vertical column in a periodic table where the elements are present is known as Group.
Chemical properties of the elements repeat themselves at regular intervals because of the electronic configuration. The elements that are present in a Group have similar chemical properties. This is because the outer-shell electronic configuration will be the same.
The periodic table has all the elements that can be distinguished based on the outer-shell electron. If the outer-shell electron is present in s subshell, then the elements are present in s area of periodic table. If the outer-shell electron is present in p subshell, then the elements are present in p area of periodic table. If the outer-shell electron is present in d subshell, then the elements are present in d area of periodic table. If the outer-shell electron is present in f subshell, then the elements are present in f area of periodic table.
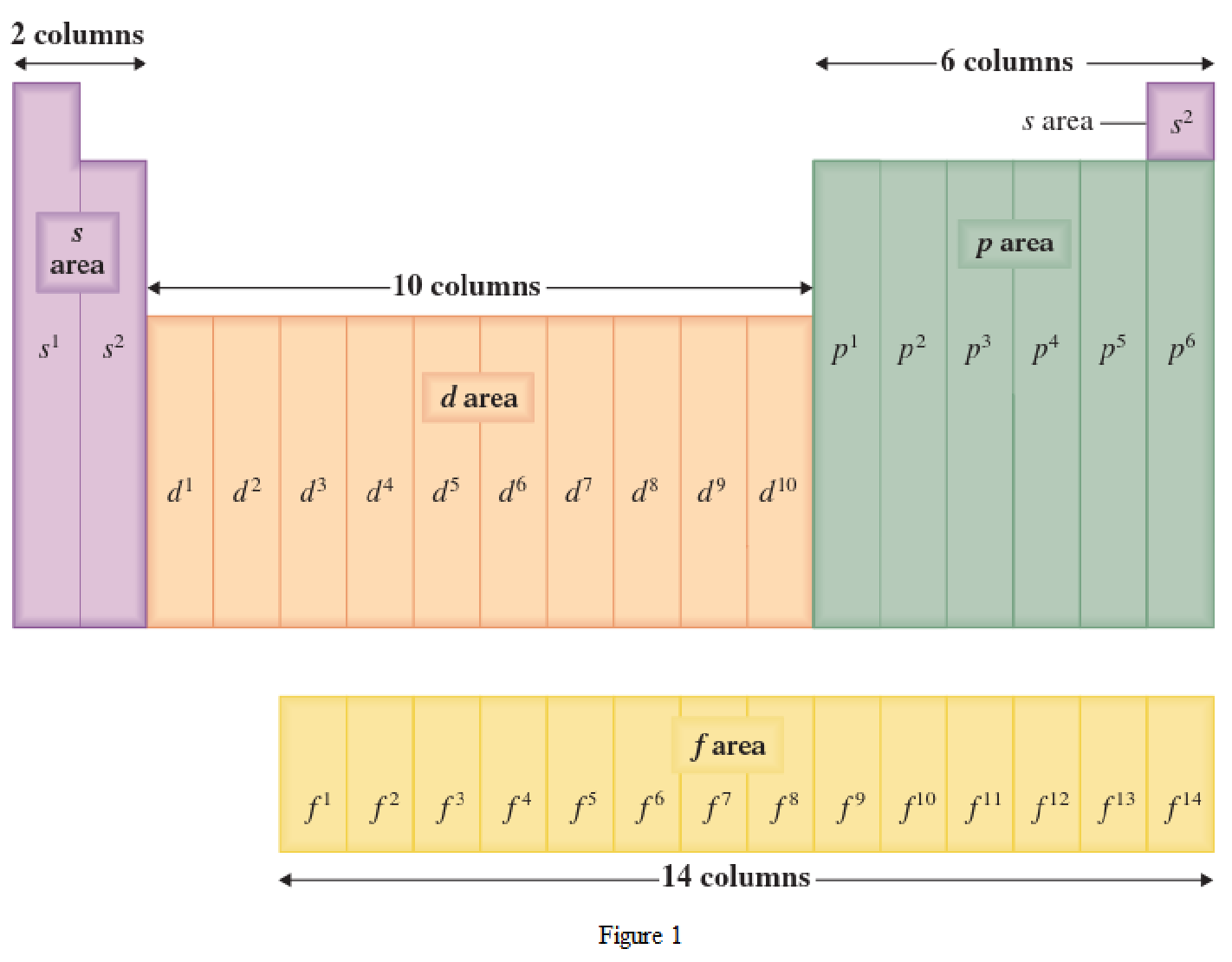
Distinguishing electron is the one that is the last electron added to the electronic configuration of an element when the electron subshells are filled in the order of increasing energy. This distinguishing electron determines the area of the element in the periodic table. This is because this only causes the element electronic configuration to differ from other elements.
(c)
Interpretation:
The element that is highlighted in red in the periodic table is a
Concept Introduction:
Periodic law states that if the elements are arranged in increasing order of atomic number, then the elements with similar chemical properties occur at regular intervals or periodic intervals. The elements are arranged in a periodic table in which the arrangement was based on the atomic number of the elements and the elements that have similar chemical properties are positioned in vertical columns.
Location of an element in a periodic table can be given by the period number and the group number. The horizontal row in a periodic table where the elements are present is known as Period. The vertical column in a periodic table where the elements are present is known as Group.
Chemical properties of the elements repeat themselves at regular intervals because of the electronic configuration. The elements that are present in a Group have similar chemical properties. This is because the outer-shell electronic configuration will be the same.
The periodic table has all the elements that can be distinguished based on the outer-shell electron. If the outer-shell electron is present in s subshell, then the elements are present in s area of periodic table. If the outer-shell electron is present in p subshell, then the elements are present in p area of periodic table. If the outer-shell electron is present in d subshell, then the elements are present in d area of periodic table. If the outer-shell electron is present in f subshell, then the elements are present in f area of periodic table.
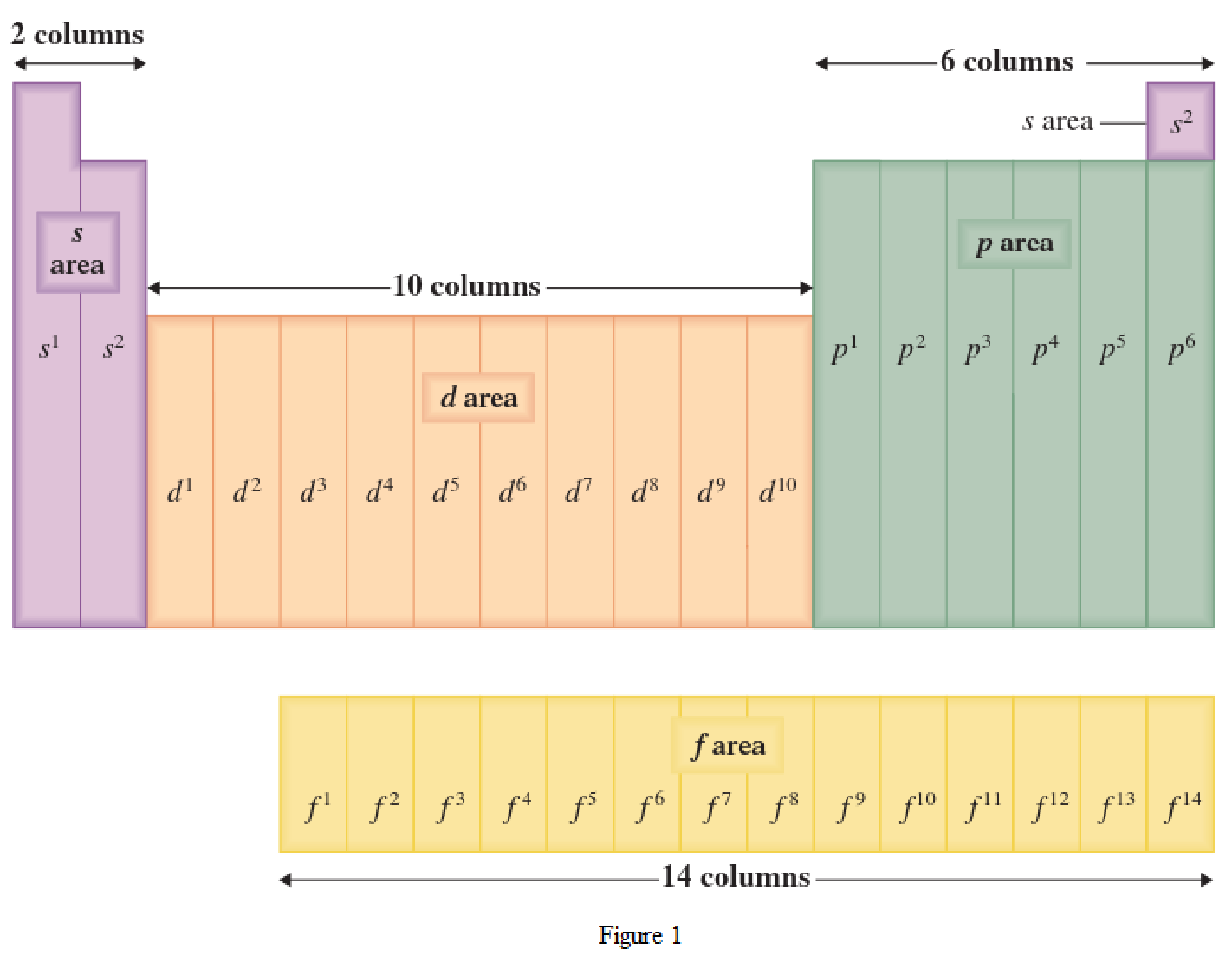
Distinguishing electron is the one that is the last electron added to the electronic configuration of an element when the electron subshells are filled in the order of increasing energy. This distinguishing electron determines the area of the element in the periodic table. This is because this only causes the element electronic configuration to differ from other elements.
(d)
Interpretation:
The element that is highlighted in green in the periodic table is a
Concept Introduction:
Periodic law states that if the elements are arranged in increasing order of atomic number, then the elements with similar chemical properties occur at regular intervals or periodic intervals. The elements are arranged in a periodic table in which the arrangement was based on the atomic number of the elements and the elements that have similar chemical properties are positioned in vertical columns.
Location of an element in a periodic table can be given by the period number and the group number. The horizontal row in a periodic table where the elements are present is known as Period. The vertical column in a periodic table where the elements are present is known as Group.
Chemical properties of the elements repeat themselves at regular intervals because of the electronic configuration. The elements that are present in a Group have similar chemical properties. This is because the outer-shell electronic configuration will be the same.
The periodic table has all the elements that can be distinguished based on the outer-shell electron. If the outer-shell electron is present in s subshell, then the elements are present in s area of periodic table. If the outer-shell electron is present in p subshell, then the elements are present in p area of periodic table. If the outer-shell electron is present in d subshell, then the elements are present in d area of periodic table. If the outer-shell electron is present in f subshell, then the elements are present in f area of periodic table.
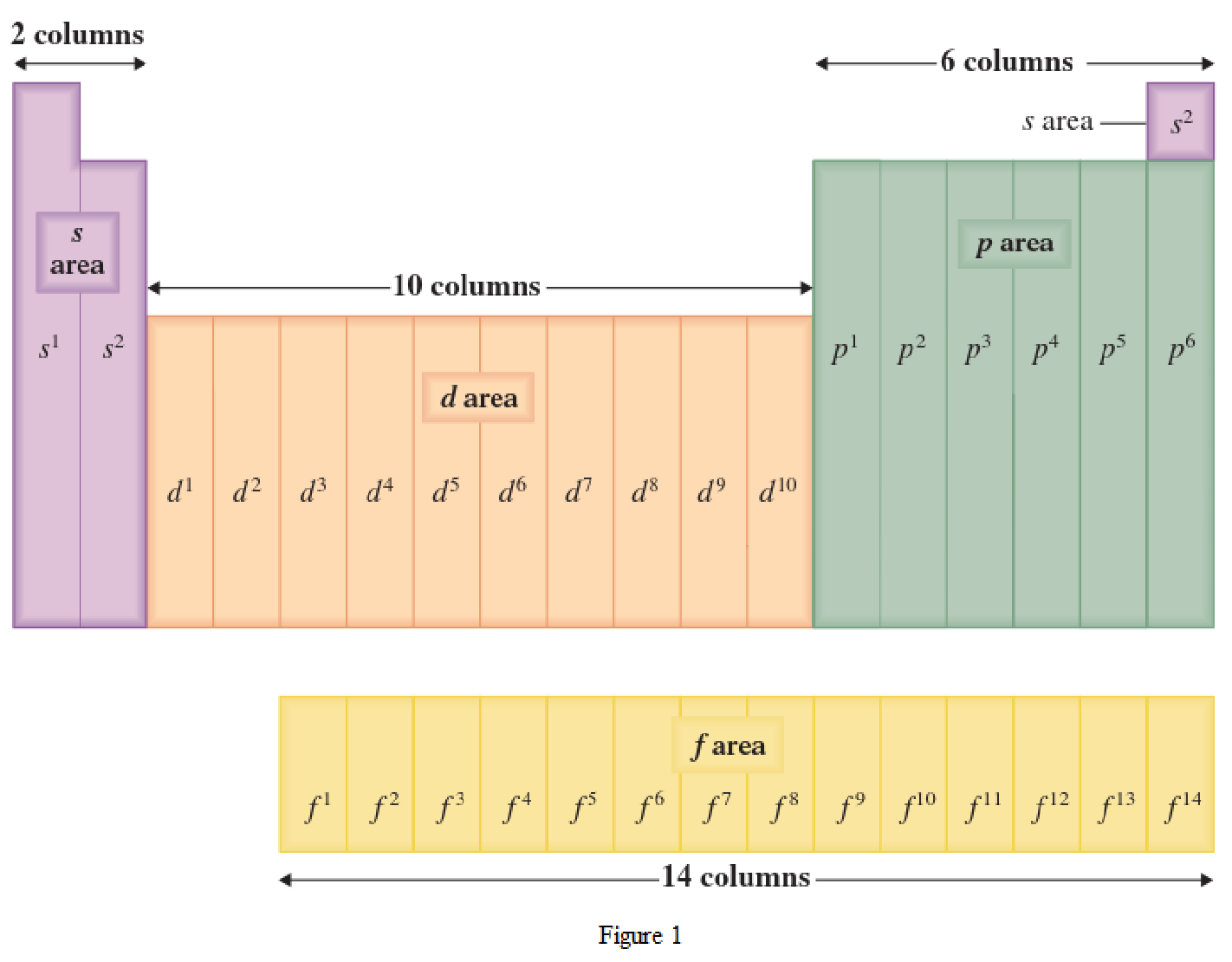
Distinguishing electron is the one that is the last electron added to the electronic configuration of an element when the electron subshells are filled in the order of increasing energy. This distinguishing electron determines the area of the element in the periodic table. This is because this only causes the element electronic configuration to differ from other elements.
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 3 Solutions
General, Organic, and Biological Chemistry
- You have a racemic mixture of d-2-butanol and l-2-butanol. The d isomer rotates polarized light by +13.5∘. What is the rotation of the polarization of light of your mixture?arrow_forwardDetermine the Atomic Packing Factor (APF) of a base-centered tetragonal crystal structure shown below. In this structure, atoms are touching along the base diagonal. The height of the unit cell is given by c and is equal to 1.54 times a. Express your answer in terms of percentage and in two decimal places only. Do not put the percentage sign.arrow_forwardThe ionization of p-nitrophenol is shown below (pKa = 7.0): a. Identify the weak acid and conjugate base. b. At pH 7, what are the relative concentrations of ionized and un-ionized p-nitrophenol? c. If enough concentrated hydrochloric acid is added to a solution of p-nitrophenol to lower the pH from 7 to 5, what will happen to the relative concentrations of the ionized and un-ionized forms? d. Ionized p-nitrophenol has a yellow color, while the un-ionized form is colorless. The yellow color can be measured using a spectrophotometer at 400nm. In order to determine the total amount of p-nitrophenol in a solution, would you perform the spectrophotometer reading at an acidic or basic pH? Clearly explain why? e. A solution of p-nitrophenol at pH 7.95 was found to have an A400 of 0.255 . What is the total concentration (in µM) of p-nitrophenol (ionized plus un-ionized) in the solution? The molar extinction coefficient of p-nitrophenol is 18,500 M-1cm-1 and the pKa is 7.arrow_forward
- Why is it not possible to find a five-fold symmetry operation in naturally-occurring crystals?arrow_forwardThe Ksp values of silver chromate Ag2CrO4 and silver iodate Ag(IO3) are given below. Ag2CrO4 Ag(IO3) Ksp 1.12 x 10-12 3.17 x 10-8 Based on these Ksp values, which of the following is true? Choose one option only. Options: a. In the solution consisting of 1.00 x10-4 M Ag+ and 5.00 x10-5 M CrO42-, Ag2CrO4 precipitate will form. b. In the solution consisting of 1.0 x10-4 M Ag+ and 1.0 x10-4 M IO3-, Ag(IO3) precipitate will form. c. In pure water, the solubility of Ag2CrO4 is lower than the solubility of Ag(IO3). d. In the solution consisting of 0.200 M CrO42- and 0.200 M IO3-, Ag2(CrO4) will precipitate first if we add Ag+ ions gradually into the above mixture.arrow_forwardA physician prescribes a prescription of Doriden, 325 mg, which requires you to prepare 30 capsules to be taken by a patient 1 hour before bedtime. Assuming that you will make a minimum of extra powder, how many tablets will you use to make this prescription? How many capsules will you calculate for? (Doriden is available in your pharmacy as a 500 mg tablet weighing 750 mg) Select one: a. 20 tablets, 30.77 capsules b. 19 tablets, 30 capsules c. 19 tablets, 32 capsules d. 20 tablets, 40 capsules What is the weight in grams of 1 Liter of alcohol (density, 0.816 g/mL? O O Oarrow_forward
- Are the following items chiral or achiral? Give a justification for your answers.(a) A fork (b) This textbook(c) Your right hand(d) A blank 3 X 5 index cardarrow_forwardThe following 'H NMR and IR spectra are obtained for an unknown compound with an empirical formula of C3H1403. Using the information given, determine the structure of the unknown compound. Show all details in your answer. a) 100 %T 88 20 35ee 3eee 25ee 2e0e 1see 1e00 cm1 2H зн 3H 2H 2H 2H 4.5 4.0 3.5 3.0 2.5 2.0 1.5 1.0 PPM 2878. 16 1716. 08 1234.60 1157.44 BE'T6 882.49arrow_forwardOne liter of a 0.1 M Tris buffer (pKa of Tris = 8.3, see Table 2.4) is prepared and adjusted to a pH of 2.0. A) What are the concentrations of the conjugate base and weak acid at this pH?Answer with 2 significant digits. I have solved for [HA] = 0.10 Can you please help solve for [A-] = ?arrow_forward
- The main constituents in vinegar are water and ethanoic acid (CH3COOH). In order to determine the concentration of acid in homemade vinegar, a student titrated 25 cm3 of 001 M NaOH against the vinegar. The equation for the reaction is: CH3COOH(aq) + NaOH(aq) ® CH3COONa(aq) + H2O(l) The following titration results were obtained: Burette readings (cm3) Rough 1 2 Final burette reading 20.10 38.90 31.40 Initial burette reading 0.10 20.00 12.50 Volume of vinegar used 20.00 18.90 18.90 (a) What volume of vinegar should be used in the calculation? (b) What is the mole ratio of NaOH:CH3COOH? (c) Calculate the number of moles of alkali in 25 cm3 of NaOH solution used. (d) How many moles of acid were used in the titration? (e) Calculate the…arrow_forwardThe molecular weight of glucose is 180.16 g/mol. Say you want to make 100 ml of a 0.6M solution of glucose. How much glucose and water should you use? Show your calculations for how you would make this solution.arrow_forwardFor the treatment of his indigestion, Tin must drink a salt solution with a pH between 8.00 to 8.50. Tan, Tin's friend, wanted to give Tin a 0.895 mM solution of a water-soluble salt generated from the ions K+ and C3H2O42-. a. Write the chemical formula of the salt offered by Tan. b. What is the hydrolysis reaction for the salt solution offered by Tan. c. What is the pH of the salt solution? (2 decimal places)arrow_forward
 Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)BiologyISBN:9780134580999Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. HoehnPublisher:PEARSON
Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)BiologyISBN:9780134580999Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. HoehnPublisher:PEARSON Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax
Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781259398629Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa StouterPublisher:Mcgraw Hill Education,
Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781259398629Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa StouterPublisher:Mcgraw Hill Education, Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)BiologyISBN:9780815344322Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter WalterPublisher:W. W. Norton & Company
Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)BiologyISBN:9780815344322Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter WalterPublisher:W. W. Norton & Company Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781260159363Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, CynthiaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co.
Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781260159363Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, CynthiaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co. Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)BiologyISBN:9781260231700Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael WindelspechtPublisher:McGraw Hill Education
Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)BiologyISBN:9781260231700Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael WindelspechtPublisher:McGraw Hill Education





