
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
The structure for the given molecule is to be drawn.
Concept introduction:
When assigning priorities to substituents, the atom having the greater
Answer to Problem C.32P
The structure of
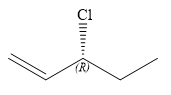
Explanation of Solution
The given name is:
In this compound, the root is pentene. The compound contains a double bond between C1 and C2 carbon atoms. The longest continuous carbon chain contains five carbon atoms. A chlorine is attached to C3 carbon atom of the root. The structure of the molecule without considering its stereochemistry is:
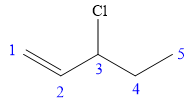
There is one chiral carbon at C3 in the above molecule. The required configuration at the chiral carbon atom is R.
At C3 carbon atom, the four substituents are:
Applying the first tiebreaker,
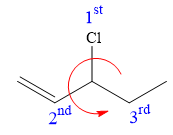
Thus, in order to have R configuration at C3 carbon atom, the first-priority substituent must be attached by a dash bond. Therefore, the correct structure for

The structure for the given name is drawn as shown above.
(b)
Interpretation:
The structure for the given molecule is to be drawn.
Concept introduction:
When assigning priorities to substituents, the atom having the greater atomic number has higher priority. In case of comparison between isotopes, the one having the greater atomic mass gets higher priority. When the fourth priority substituent is pointing away (it is attached by a dash bond) and the first, second, and third priority substituents are arranged clockwise, the configuration is R. When the fourth priority substituent is pointing away (it is attached by a dash bond) and the first, second, and third priority substituents are arranged counterclockwise, the configuration is S. If the fourth priority substituent is attached by a wedge bond, then the clockwise or counterclockwise arrangement of the first, second, and third priority substituents is determined and that arrangement is reversed before assigning R or S. If the fourth priority substituent is in the plane of the page, then it is switched with the substituent that points away. Then the clockwise or counterclockwise arrangement of the first, second and third priority substituents is determined and that arrangement is reversed before assigning R or S. When writing the IUPAC name, the R or S designation is written in parenthesis for each asymmetric carbon atom and hyphens are used to separate those designations from the rest of the IUPAC name.
Answer to Problem C.32P
The structure of
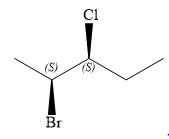
Explanation of Solution
The given name is
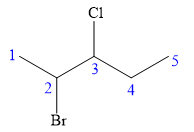
There are two chiral carbon atoms at C2 and C3 in the above molecule. The required configuration at both the chiral carbon atoms is S.
At C2 carbon atom, the four substituents are:
Applying the first tiebreaker,
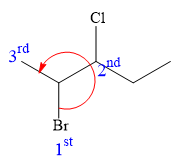
Thus, in order to maintain this arrangement of substituents at the C2 carbon atom, the fourth-priority substituent must be attached by a dash bond
At C3 carbon atom, the four substituents are:
Applying the first tiebreaker,
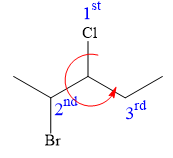
Thus, in order to maintain this arrangement of substituents at the C3 carbon atom, the fourth-priority substituent must be attached by a dash bond
Therefore, the correct structure for

The structure for the given name is drawn as shown above.
(c)
Interpretation:
The structure for the given molecule is to be drawn.
Concept introduction:
When assigning priorities to substituents, the atom having the greater atomic number has higher priority. In case of comparison between isotopes, the one having the greater atomic mass gets higher priority.
When the fourth priority substituent is pointing away (it is attached by a dash bond) and the first, second, and third priority substituents are arranged clockwise, the configuration is R.
When the fourth priority substituent is pointing away (it is attached by a dash bond) and the first, second, and third priority substituents are arranged counterclockwise, the configuration is S.
If the fourth priority substituent is attached by a wedge bond, then the clockwise or counterclockwise arrangement of the first, second, and third priority substituents is determined and that arrangement is reversed before assigning R or S.
If the fourth priority substituent is in the plane of the page, then it is switched with the substituent that points away. Then the clockwise or counterclockwise arrangement of the first, second and third priority substituents is determined and that arrangement is reversed before assigning R or S. When writing the IUPAC name, the R or S designation is written in parenthesis for each asymmetric carbon atom and hyphens are used to separate those designations from the rest of the IUPAC name.
Answer to Problem C.32P
The structure of
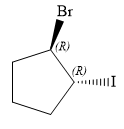
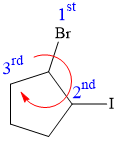
Explanation of Solution
The given name is:
In this compound, the root is cyclopentane. One bromine atom and one iodine atom is attached to C1 and C2 carbon atom of the root.
The structure of the molecule, without considering its stereochemistry, is:
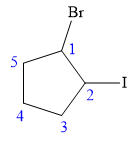
There are two chiral carbon atoms at C1 and C2 in the above molecule. The required configuration at both the chiral carbon atoms is R.
At C1 carbon atom, the four substituents are:
Applying the first tiebreaker,
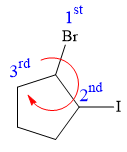
Thus, in order to maintain this arrangement of substituents at C2 carbon atom, the fourth-priority substituent must be attached by a dash bond
At C3 carbon atom, the four substituents are:
Applying the first tiebreaker,

Thus, in order to maintain this arrangement of substituents at the C3 carbon atom, the fourth-priority substituent must be attached by a dash bond
Therefore, the correct structure for
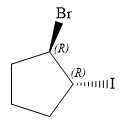
The structure for the given name is drawn as shown above.
(d)
Interpretation:
The structure for the given molecule is to be drawn.
Concept introduction:
When assigning priorities to substituents, the atom having the greater atomic number has higher priority. In case of comparison between isotopes, the one having the greater atomic mass gets higher priority. When the fourth priority substituent is pointing away (it is attached by a dash bond) and the first, second, and third priority substituents are arranged clockwise, the configuration is R. When the fourth priority substituent is pointing away (it is attached by a dash bond) and the first, second, and third priority substituents are arranged counterclockwise, the configuration is S. If the fourth priority substituent is attached by a wedge bond, then the clockwise or counterclockwise arrangement of the first, second, and third priority substituents is determined and that arrangement is reversed before assigning R or S. If the fourth priority substituent is in the plane of the page, then it is switched with the substituent that points away. Then the clockwise or counterclockwise arrangement of the first, second, and third priority substituents is determined and that arrangement is reversed before assigning R or S. When writing the IUPAC name, the R or S designation is written in parenthesis for each asymmetric carbon atom and hyphens are used to separate those designations from the rest of the IUPAC name.
Answer to Problem C.32P
The structure of
Explanation of Solution
The given name is:
In this compound, the root is cyclohexene. The cyclohexane ring contains one double bond between C1 and C2 carbon atoms. One chlorine atom is attached at the C3 carbon atom of the root. The structure of the molecule without considering its stereochemistry is:
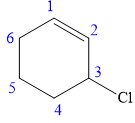
There is one chiral carbon at C3 in the above molecule. The required configuration at the chiral carbon atom is S.
At C3 carbon atom, the four substituents are:
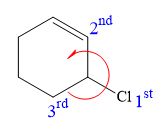
Thus, in order to maintain this arrangement of substituents at the C2 carbon atom, the first priority substituent should be attached by a dash bond. Therefore, the correct structure for
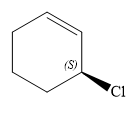
The structure for the given name is drawn as shown above.
(e)
Interpretation:
The structure for the given molecule is to be drawn.
Concept introduction:
When assigning priorities to substituents, the atom having the greater atomic number has higher priority. In case of comparison between isotopes, the one having the greater atomic mass gets higher priority. When the fourth priority substituent is pointing away (it is attached by a dash bond) and the first, second, and third priority substituents are arranged clockwise, the configuration is R. When the fourth priority substituent is pointing away (it is attached by a dash bond) and the first, second, and third priority substituents are arranged counterclockwise, the configuration is S. If the fourth priority substituent is attached by a wedge bond, then the clockwise or counterclockwise arrangement of the first, second, and third priority substituents is determined and that arrangement is reversed before assigning R or S. If the fourth priority substituent is in the plane of the page, then it is switched with the substituent that points away. Then the clockwise or counterclockwise arrangement of the first, second, and third priority substituents is determined and that arrangement is reversed before assigning R or S. When writing the IUPAC name, the R or S designation is written in parenthesis for each asymmetric carbon atom and hyphens are used to separate those designations from the rest of the IUPAC name.
Answer to Problem C.32P
The structure of
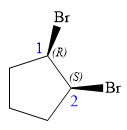
Explanation of Solution
The given name is:
In this compound, the root is cyclopentane. Two bromine atoms are attached at C1 and C2 carbon atoms of the root. The structure of the molecule without considering its stereochemistry is:
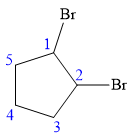
There are two chiral carbon atoms at C1 and C2 carbon atoms. The required configuration at C1 is R and that at C2 is S.
At C1 carbon atom, the four substituents are:
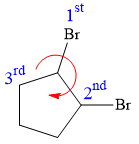
Thus, in order to have R configuration, and maintain this arrangement of substituents at the C1 carbon atom, the first-priority substituent must be attached by a wedge bond.
At C2 carbon atom, the four substituents are:
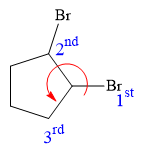
Thus, in order to have R configuration, and maintain this arrangement of substituents at the C1 carbon atom, the first-priority substituent must be attached by a dash bond.
Therefore, the correct structure for

The structure for the given name is drawn as shown above.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter C Solutions
Organic Chemistry: Principles and Mechanisms (Second Edition)
- Draw the structures for each of the following molecules. (a) fluorobenzene; (b) 1-chloro-2-fluorobenzene;(c) 1-iodo-4-nitrobenzene; (d) 1,3-dibromobenzene; (e) 2,3-dimethyl-1-cyclopentylbenzene; (f) 4-ethoxy-1,2-dinitrobenzenearrow_forwardDraw the structure of each of the following molecules (a) 2,2-dimethylcyclopentane-1-carboxylic acid;(b) (R)-3-chloropentanoic acid; (c) (2R,3S)-2,3-dinitrobutanedioic acidarrow_forwardQ1: Draw the structure of each of the following molecules: (a) (R)-1-chloro-1-fluorobutane (c) (2R,3S)-3-Bromo-2-chloro-1-pentanol (b) (S)-2-chloropentane; (d) (R)-2,2,3-trichlorobutane.arrow_forward
- (a) which if the structure of trans-1,2-dimethylcyclopentane? (b) which is the most stable conformation of 1-bromo-2-ethylcyclohexane? (c) which is the least stable conformation of 1-bromo-2-ethylcyclohexane? (d) which is the more stable configuration of 1,3-dimethylcyclopentane? *Et = ethylarrow_forwardDraw the molecule that corresponds to each IUPAC name. (a) 2,3-dimethylcyclopentanone; (b) 4,4-difluoroheptanal;(c) 1,1,1-trichloropentan-3-one; (d) (1S,3S)-3-ethoxycyclohexanecarbaldehydearrow_forward(a) Draw and name all five isomers of formula C3H5F.(b) Draw all 12 acyclic (no rings) isomers of formula C4H7Br. Include stereoisomers.arrow_forward
- What reagents are needed to convert 1-ethylcyclohexene into (a) 1-bromo-2ethylcyclohexane; (b) 1-bromo-1-ethylcyclohexane; (c) 1,2-dibromo-1-ethylcyclohexane?arrow_forward2) Draw the molecule that corresponds to (3R,5R,6R)-5-cyclopropyl-6-ethyl-3-iodo-1-methylcyclohex-1-ene.arrow_forwardDraw the structures for these molecules. (a) 2-chloropropene; (b) 3-methylbut-1-ene; (c) 2,3-dimethyl-2-butene;(d) 2-ethoxy-3,3-dimethylcyclohexene; (e) 3,4,5-trimethoxycycloheptene; (f) 3-bromo-2-methyl-4-nitrocyclopentene;(g) 3,3-dibromo-4-methylcyclopentene; (h) 4-methyl-2-pentynearrow_forward
- Draw the structures of the following compounds. (a) 1-isobutyl-4-isopropylcyclohexane; (b) tert-butylcyclopentane;(c) 3,3-diisopropyloctanearrow_forward(a) 4-Bromo-2-hexene (Z), (R) isomer name: (Z), (S) isomer name: (E), (R) isomer name: (E), (S) isomer name:arrow_forwardDraw the most stable conformation of cis-1-tert-butyl-3-ethylcyclohexane. (a) (b) trans-1-tert-butyl-2-methylcyclohexane. (c) trans-1-tert-butyl-3-(1,1-dimethylpropyl)cyclohexane.arrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





