
a)
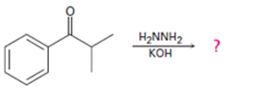
Interpretation:
The product of the Wolff-Kishner reduction reaction shown is to be given. The electron-pushing mechanism, beginning from the hydrazone intermediate is to be provided.
Concept introduction:
In Wolff-Kishner reduction
To give:
The product of the Wolff-Kishner reduction reaction shown.
To provide:
The electron-pushing mechanism, beginning from the hydrazone intermediate.
Answer to Problem 38MP
The product of the Wolff-Kishner reduction reaction shown is
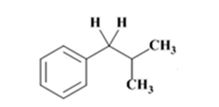
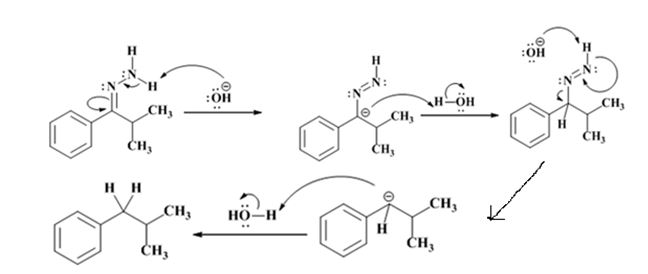
The electron-pushing mechanism for the formation of the alkane, beginning from the hydrazone intermediate, is given below.
Explanation of Solution
The hydroxide ion from KOH abstracts a weakly acidic H from –NH2 of the hydrazone of isopropyl phenyl ketone to yield a carbanion which picks up a proton to yield a neutral intermediate. Deprotonation of the remaining hydrogen on N by the hydroxide ion occurs with the eliminartion of nitrogen to yield another carbanion which is protonated to give the alkane, ethyl benzene, as the product.
The product of the Wolff-Kishner reduction reaction shown is

The electron-pushing mechanism, beginning from the hydrazone intermediate is given below.

b)
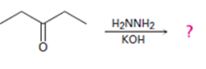
Interpretation:
The product of the Wolff-Kishner reduction reaction shown is to be given. The electron-pushing mechanism, beginning from the hydrazone intermediate is to be provided.
Concept introduction:
In Wolff-Kishner reduction aldehydes and ketones react with hydrazine in the presence of a base to yield alkanes. First a hydrazone is formed which is then converted into an alkane.
To give:
The product of the Wolff-Kishner reduction reaction shown.
To provide:
The electron-pushing mechanism the formation of the alkane beginning from the hydrazone intermediate.
Answer to Problem 38MP
The product of the Wolff-Kishner reduction reaction shown is
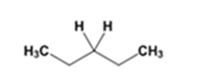
The electron-pushing mechanism the formation of the alkane, beginning from the hydrazone intermediate, is given below.
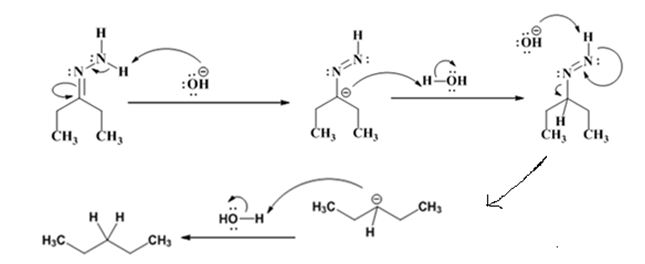
Explanation of Solution
The hydroxide ion from KOH abstracts a weakly acidic H from –NH2 of the hydrazone of diethyl ketone to yield a carbanion which picks up a proton to yield a neutral intermediate. Deprotonation of the remaining hydrogen on N by the hydroxide ion occurs with the eliminartion of nitrogen to yield another carbanion which is protonated to give the alkane, n-pentane, as the product.
The product of the Wolff-Kishner reduction reaction shown is

The electron-pushing mechanism, beginning from the hydrazone intermediate is given below.

c)
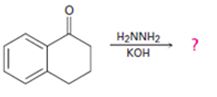
Interpretation:
The product of the Wolff-Kishner reduction reaction shown is to be given. The electron-pushing mechanism, beginning from the hydrazone intermediate is to be provided.
Concept introduction:
In Wolff-Kishner reduction aldehydes and ketones react with hydrazine in the presence of a base to yield alkanes. First a hydrazone is formed which is then converted into an alkane.
To give:
The product of the Wolff-Kishner reduction reaction shown.
To provide:
The electron-pushing mechanism the formation of the alkane beginning from the hydrazone intermediate.
Answer to Problem 38MP
The product of the Wolff-Kishner reduction reaction shown is
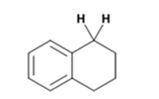
The electron-pushing mechanism the formation of the alkane, beginning from the hydrazone intermediate, is given below.
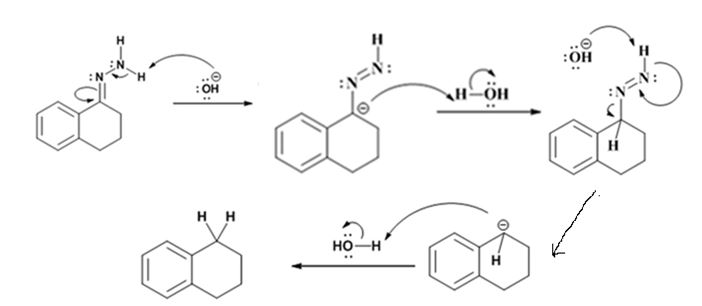
Explanation of Solution
The hydroxide ion from KOH abstracts a weakly acidic H from –NH2 of the hydrazone of the ketone to yield a carbanion which picks up a proton to yield a neutral intermediate. Deprotonation of the remaining hydrogen on N by the hydroxide ion occurs with the eliminartion of nitrogen to yield another carbanion which is protonated to give the alkane as the product.
The product of the Wolff-Kishner reduction reaction shown is

The electron-pushing mechanism, beginning from the hydrazone intermediate is given below.

d)
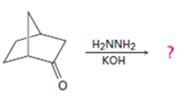
Interpretation:
The product of the Wolff-Kishner reduction reaction shown is to be given. The electron-pushing mechanism, beginning from the hydrazone intermediate is to be provided.
Concept introduction:
In Wolff-Kishner reduction aldehydes and ketones react with hydrazine in the presence of a base to yield alkanes. First a hydrazone is formed which is then converted into an alkane.
To give:
The product of the Wolff-Kishner reduction reaction shown.
To provide:
The electron-pushing mechanism, beginning from the hydrazone intermediate.
Answer to Problem 38MP
The product of the Wolff-Kishner reduction reaction shown is
The electron-pushing mechanism for the formation of the alkane beginning from the hydrazone intermediate, is given below.
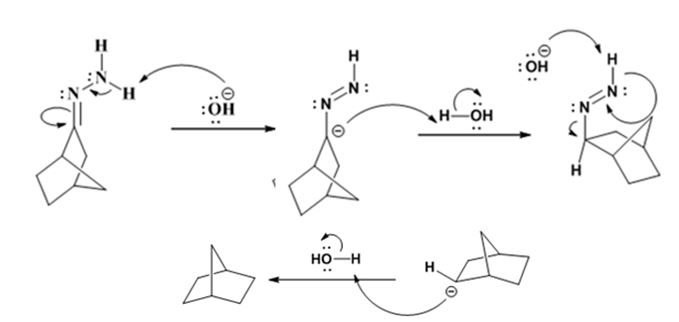
Explanation of Solution
The hydroxide ion from KOH abstracts a weakly acidic H from –NH2 of the hydrazone of ketone to yield a carbanion which picks up a proton to yield a neutral intermediate. Deprotonation of the remaining hydrogen on N by the hydroxide ion occurs with the eliminartion of nitrogen to yield another carbanion which is protonated to give the alkane as the product.
The product of the Wolff-Kishner reduction reaction shown is

The electron-pushing mechanism for the formation of the alkane beginning from the hydrazone intermediate, is given below.

Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 19 Solutions
Organic Chemistry
- Enamines normally react with methyl iodide to give two products: one arising from alkylation at nitrogen and the second arising from alkylation at carbon. For example, Heating the mixture of C-alkylation and N-alkylation products gives only the product from C-alkylation. Propose a mechanism for this isomerization.arrow_forwardObtain derivatives or oxidation-reduction products from acetophenone (C6H5COCH3) in four different ways using suitable reagents and appropriate reactions. Write down the mechanism of the one you want in detail.arrow_forward3. cyclohexanone to cyclohexane. A second year chemistry student is assigned a task to prepare compound 2 from compound 1 using lithium aluminium hydride as a reducing agent. However, from the reaction mixture, no traces of product 2 were detected. Explain this observation in detail and suggest an alternative route that will lead to product 2. H 1 CH3 LiAllH4 H O: 2 CH3 quearrow_forward
- Which products are obtained by the following reactions (a) and (b)? Specify the expected main product, if several products can be formed.arrow_forwardProvide a step-by-step mechanism to account for the product of the following reaction. Show the structure of each of the intermediates and use curved arrows to indicate electron flow in each of these stepsarrow_forwardProvide mechanisms for the following reactions, pleasearrow_forward
- The following reaction was performed as part of a research program sponsored by the National Institutes of Health to develop therapeutic agents for the treatment of cocaine addiction. Using what you have seen about the reactions of halogens with alkenes, propose a mechanism for this process.arrow_forwardWrite the products of the following Cope rearrangements; pay particular attention to the stereochemistry in the products. Predict which is preferred.arrow_forward27) Give the products of the reaction and provide a step-by-step mechanism for the formation of the products. O not + H₂O HCIarrow_forward

 Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning

