
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:The curved arrows for acid-base reaction below should be added.
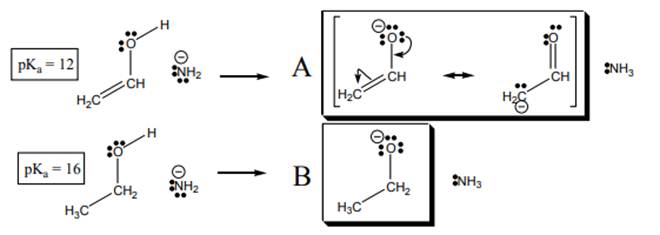
Concept introduction:According to Bronsted-Lowry concept, substance that donates proton is termed as acid while that accepts or gains protons is called base. Species formed after loss of protons from acids are known as their respective conjugate bases whereas conjugate acid is produced by addition of protons to base.
(b)
Interpretation: The alcohol that is stronger acid from below alcoholson the basis of
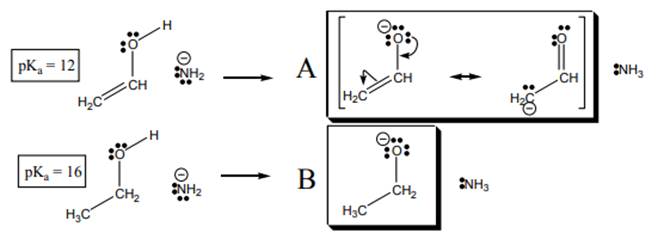
Concept introduction:The dissociation constant of acid represents strength of acid in solution. It is denoted by
(c)
Interpretation: The conjugate base that has lower potential energy in below reactionshould be determined.
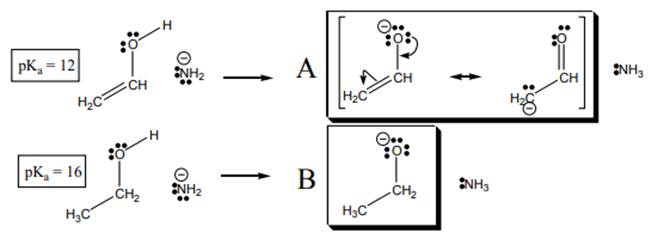
Concept introduction:When one single structure is unable to describe all the properties of single molecule, a phenomenon called resonance comes into play. This arises when two or more than two Lewis structures are possible for one molecule. All such structures are called resonating structures and have same placement of atoms in them but these have different locations of bond pairs and lone pairs. The resonating structures are inter-convertible with each other. The resultant of all the resonating or contributing structures is called the resonance hybrid.
(d)
Interpretation: The relation between below exampleand story should be explained.
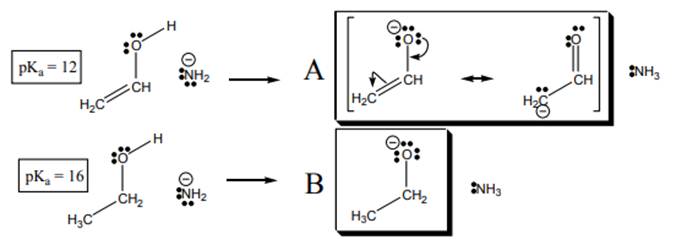
Concept introduction:When one single structure is unable to describe all the properties of single molecule, a phenomenon called resonance comes into play. This arises when two or more than two Lewis structures are possible for one molecule. All such structures are called resonating structures and have same placement of atoms in them but these have different locations of bond pairs and lone pairs. The resonating structures are inter-convertible with each other. The resultant of all the resonating or contributing structures is called the resonance hybrid.
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 5 Solutions
Organic Chemistry: A Guided Inquiry
- For each molecule below, draw the conjugate acid or conjugate base or both if the molecule hasboth a conjugate acid and a conjugate base (e.g., water).arrow_forwardDraw the structure of the conjugate base of water. (Note that it does not appear in Figure 4.11).arrow_forwardPhenol (shown below) has a pKa10 . a. Based on pKa data, is phenol a stronger or weaker acid than an ordinaryalcohol (e.g.. CH3OH ) or water? b. Draw the conjugate base of phenol (called phenoxide) including allimportant resonance structures. c. Construct an explanation for why phenol is a stronger acid than anordinary alcohol. (You may want to consider first why phenoxide is lowerin PE than methoxide (RO) or hydroxide (HO) .arrow_forward
- Complete the equation for the reaction between each Lewis acid-base pair. In each equation, label which starting material is the Lewis acid and which is the Lewis base; use curved arrows to show the flow of electrons in each reaction. In doing this problem, it is essential that you show valence electrons for all atoms participating in each reaction. (a) (b) (c) (d)arrow_forwardAnswer questions a-c about the Bronsted acid-base reaction below using the identifying letters A-D below each structure. A table of pK₂ values for various organic and inorganic acids can be found in the references section. A phenol OH Submit Answer HO B bicarbonate C phenoxide HO a) The weaker base is b) Its conjugate acid is c) The species that predominate at equilibrium are (two letters, e.g. AC) D carbonic acid 'OH Retry Entire Group 5 more group attempts remaining Previous Next Save and Exitarrow_forward6. Rank the indicated a-H's from most to least acidic (most acidic= 1). Be sure to explain your rankings for each by drawing significant resonance structures for the conjugate base and commenting on any other factors that contribute to your rankings. H H H H. A B Cmpd Rank Resonance Structures Reasoning A Вarrow_forward
- 3. Circle the most acidic proton(s) in the molecule given below and draw the corresponding conjugate base. Then, draw three additional major resonance contributors of the conjugate base. O= H conjugate basearrow_forward6. Each of these is an erroneous attempt to show the most likely acid base reaction. a. Briefly explain what is wrong with the reaction/curved arrows as shown. b. Redraw the reaction/curved arrows, correcting all errors, and draw the correct products e. Label your curved arrows with pKa/sign and give a AH... estimate in the box. Rxn A Explanation Conected reaction Rxn B Explanation H Corted reaction ONH₂ Han AH rusarrow_forwardAnswer questions a-c about the Bronsted acid-base reaction below using the identifying letters A-D below each structure. A table of pK₂ values for various organic and inorganic acids can be found in the references section. OH hydroxide + CH3 H₂ NO₂ nitroethane HOH C water + a) The weaker base is b) Its conjugate acid is c) The species that predominate at equilibrium are (two letters, e.g. AC) CH₂ D nitroethane anionarrow_forward
- Draw the mechanism showing the Brønsted acid/base reaction between propanoic acid and methylamine. Label the acid, base, conjugate base, and conjugate acid. Show all curved arrows, lone pairs and nonzero formal charges. HO. CH;NH2 methylamine propanoic acid pKa = 4.9 Mechanism: uerm lo noits adi ol maie Using the pKa information provided/pKa tables (table appended to the end of this document), determine whether the starting reagents (propanoic acid and methyl amine) or products would be favored at equilibrium (no math needed!).arrow_forward.A justification for the rankings based on the factors that influence the relative stability of the different conjugate bases. I need to answer these for C3H5ClO2, ClCH2CO2, and CH3COOH. (Acetic acid, 3-chloropropanic, and chloroacetic acid). Pleaseeee help I will definitely ratearrow_forwardI need help on C D). Consider the three compounds above. Which compound is the most basic? Which compound is least basic? Briefly explain your reasoning on both parts.arrow_forward
 Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning

