
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
The curved arrow mechanism for the given reaction is to be shown.
Concept Introduction:
Neighbouring group participation is the interaction of the lone pair electrons of an atom (hetero) or electron present in sigma and pi bond with the parent molecule to increase the
Answer to Problem 11.77AP
The curved arrow mechanism for the reaction is shown below.
Explanation of Solution
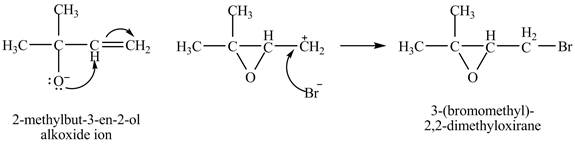
The given reaction is shown below.
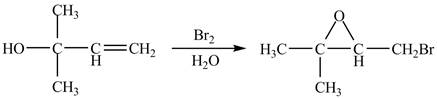
Figure 1
The oxygen atom of the alkoxide ion attack carbon of double bond to form

Figure 2
The curved arrow mechanism for given reaction is shown in Figure 2.
(b)
Interpretation:
The curved arrow mechanism for the given reaction is to be shown.
Concept Introduction:
Neighbouring group participation is -the interaction of the lone pair electrons of an atom (hetero) or electron present in sigma and pi bond with the parent molecule to increase the speed of the reaction. It is also known as anchimeric assistance.
Answer to Problem 11.77AP
The curved arrow mechanism for the given reaction is shown below.
Explanation of Solution
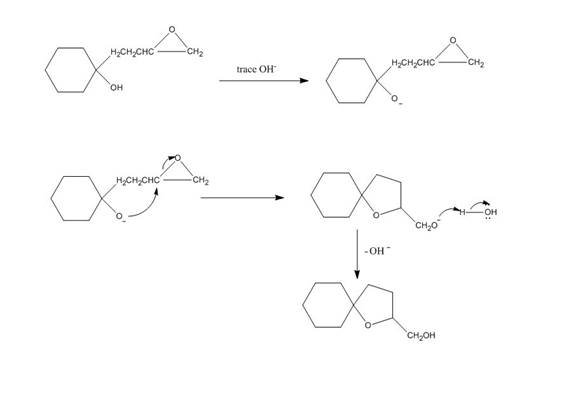
The given reaction is shown below.
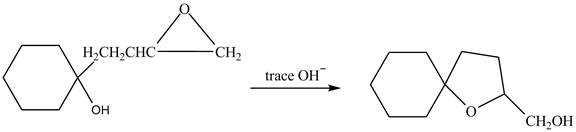
Figure 3
Hydroxide ion abstract the proton from hydroxyl group of given compound. The oxide attacks the carbon of epoxide ring to form a five membered ring. The alkoxide ion formed is protonated in presence of water. The curved arrow mechanism of the given reaction is shown below.
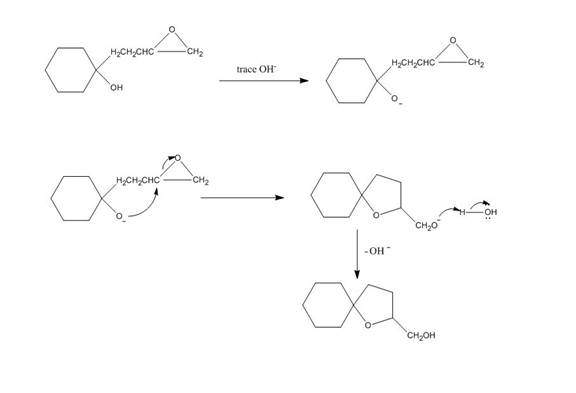
Figure 4
The curved arrow mechanism for given reaction is shown in Figure 4.
(c)
Interpretation:
The curved arrow mechanism for the given reaction is to be shown.
Concept Introduction:
Neighbouring group participation is -the interaction of the lone pair electrons of an atom (hetero) or electron present in sigma and pi bond with the parent molecule to increase the speed of the reaction. It is also known as anchimeric assistance.
Answer to Problem 11.77AP
The curved arrow mechanism of the given reaction is shown below.
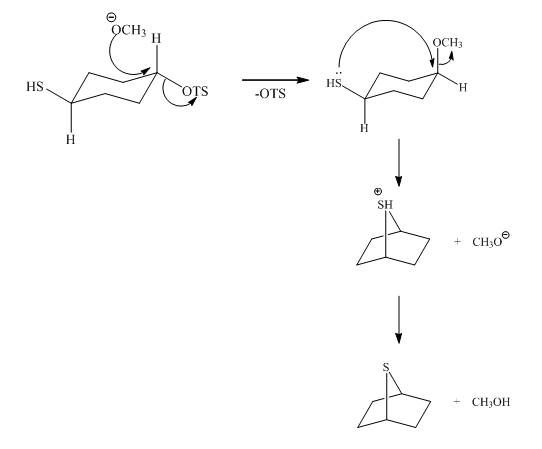
Explanation of Solution
The given reaction is shown below.
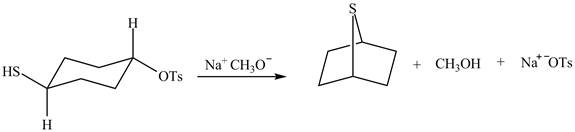
Figure 5
The methoxy group attacks the carbon containing sulfonate ester group. The nucleophilic displacement reaction occurs. The sulfonate ester group is displaced by methoxy group. Then neighbouring group participation of sulfur atom displaces the methoxy group. The sulfonium ion formed undergoes deprotonation to form the product. The curved arrow mechanism of the given reaction is shown below.

Figure 6
The curved arrow mechanism for given reaction is shown in Figure 6.
(d)
Interpretation:
The curved arrow mechanism for the given reaction is to be shown.
Concept Introduction:
Neighbouring group participation is -the interaction of the lone pair electrons of an atom (hetero) or electron present in sigma and pi bond with the parent molecule to increase the speed of the reaction. It is also known as anchimeric assistance.
Answer to Problem 11.77AP
The curved arrow mechanism of the given reaction is shown below.
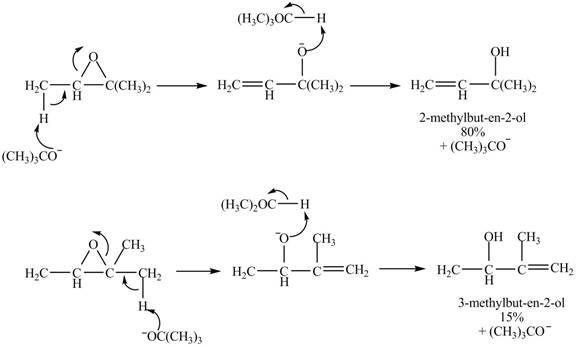
Explanation of Solution
The given reaction is shown below.
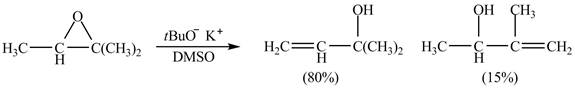
Figure 7
A strong base is used in the reaction; hence elimination reaction will take place. The given compound contains two
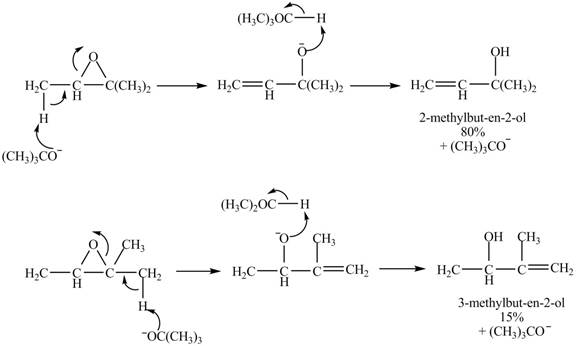
Figure 8
The curved arrow mechanism for given reaction is shown in Figure 8.
(e)
Interpretation:
The curved arrow mechanism for the given reaction is to be shown.
Concept Introduction:
Neighbouring group participation is -the interaction of the lone pair electrons of an atom (hetero) or electron present in sigma and pi bond with the parent molecule to increase the speed of the reaction. It is also known as anchimeric assistance.
Answer to Problem 11.77AP
The curved arrow mechanism of the given reaction is shown below.
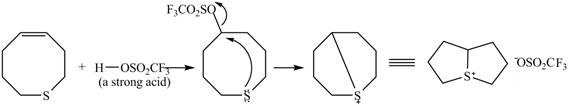
Explanation of Solution
The given reaction is shown below.
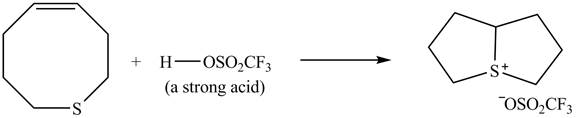
Figure 9
The
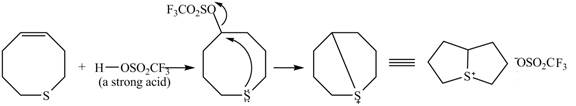
Figure 10
The curved arrow mechanism for given reaction is shown in Figure 10.
(f)
Interpretation:
The curved arrow mechanism for the given reaction is to be shown.
Concept Introduction:
Neighbouring group participation is -the interaction of the lone pair electrons of an atom (hetero) or electron present in sigma and pi bond with the parent molecule to increase the speed of the reaction. It is also known as anchimeric assistance.
Answer to Problem 11.77AP
The curved arrow mechanism of the given reaction is shown below.
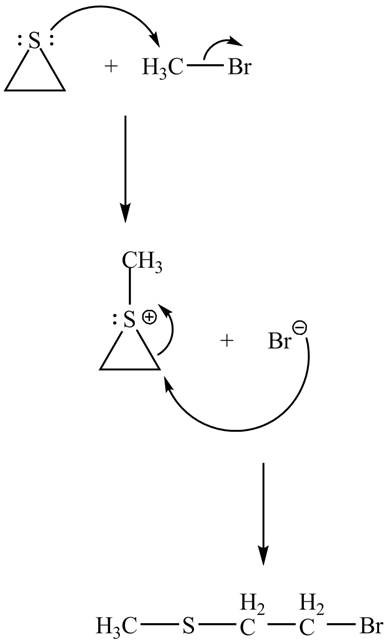
Explanation of Solution
The given reaction is shown below.
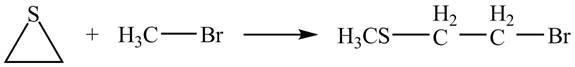
Figure 11
The lone pair of sulphur atom attacks the carbon of methyl bromide. The sulfur atom of the ring gets methylated. Then bromide ion attacks the carbon atom of ring which results in ring opening to form the desired product. The curved arrow mechanism of the given reaction is shown below.

Figure 12
The curved arrow mechanism for given reaction is shown in Figure 12.
(g)
Interpretation:
The curved arrow mechanism for the given reaction is to be shown.
Concept Introduction:
Neighbouring group participation is -the interaction of the lone pair electrons of an atom (hetero) or electron present in sigma and pi bond with the parent molecule to increase the speed of the reaction. It is also known as anchimeric assistance.
Answer to Problem 11.77AP
The curved arrow mechanism of the given reaction is shown below.
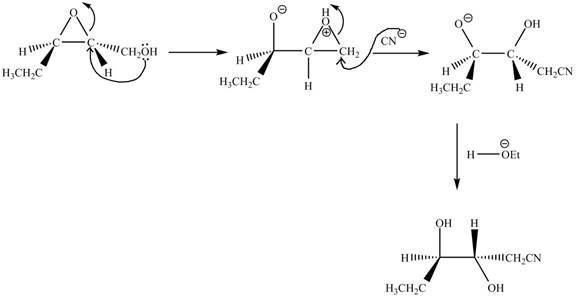
Explanation of Solution
The given reaction is shown below.
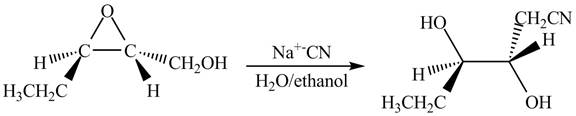
Figure 13
The neighbouring group participation of oxygen atom takes place in the given reaction. The oxygen atom of hydroxyl group attacks the electrophilic carbon atom of the epoxide ring which results in the formation of new epoxide ring. Then cyanide ion attacks at the electrophilic carbon of epoxide which results in ring opening. The oxide ion takes proton form ethanol to form desired product. The curved arrow mechanism for given reaction is shown below.

Figure 14
The curved arrow mechanism for given reaction is shown in Figure 14.
(h)
Interpretation:
The curved arrow mechanism for the given reaction is to be shown.
Concept Introduction:
Neighbouring group participation is -the interaction of the lone pair electrons of an atom (hetero) or electron present in sigma and pi bond with the parent molecule to increase the speed of the reaction. It is also known as anchimeric assistance.
Answer to Problem 11.77AP
The curved arrow mechanism of the given reaction is shown below.
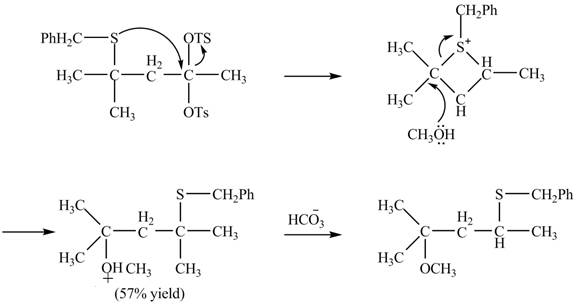
Explanation of Solution
The given reaction is shown below.
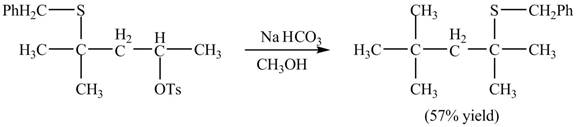
Figure 15
The sulfur atom attacks at the electrophilic carbon atom to form a four membered ring. The nucleophilic attack by methanol at the ring results in ring opening. Then the base abstracts proton from the protonated hydroxyl group to form the desired product. The curved-arrow mechanism for the given reaction is shown below.
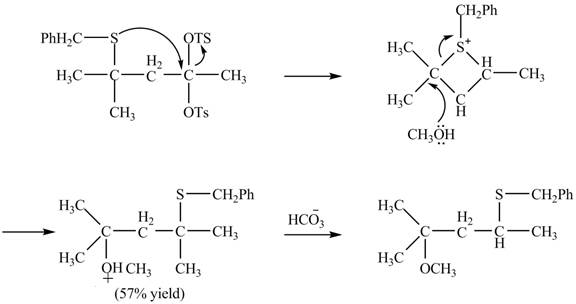
Figure 16
The curved arrow mechanism for given rearrangement is shown in Figure 16.
(i)
Interpretation:
The curved arrow mechanism for the given reaction is to be shown.
Concept Introduction:
The vicinal
Answer to Problem 11.77AP
The curved arrow mechanism of the given reaction is shown below.
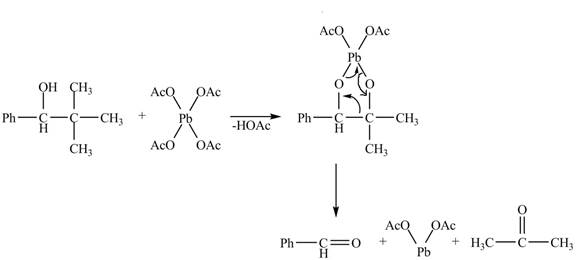
Explanation of Solution
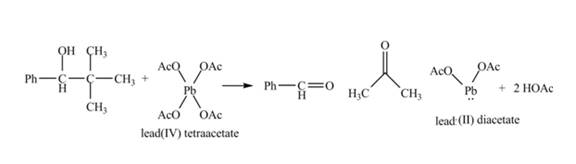
Figure 17
The given compound is a vicinal diol. It will react with the lead tetraacetate to form five membered ring intermediate. The intermediate formed rearranges to form acetone, benzaldehyde and lead diacetate. The curved arrow mechanism for the given reaction is shown below.
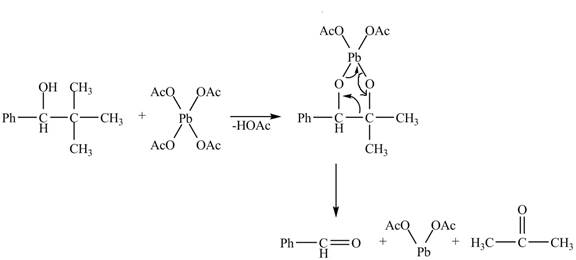
Figure 18
The curved arrow mechanism for given reaction is shown in Figure 18.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 11 Solutions
Organic Chemistry
- Provide the curved-arrow mechanism to account for the following electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction. .CI Cl2 FeCl3arrow_forwardCompound A produce compound D while undergo Friedel Crafts Alkylation. Compound D is then oxidized and produce compound E (C11H12O3) as a major product.What are the possible structural formula of compound D and E?arrow_forward(i) Explain why a high reaction temperature favours elimination reactions, instead of substitution reactions. (ii) Explain why polar aprotic solvents favour Sn2 reaction but not favour SN1 reaction.arrow_forward
- Provide the appropriate reagents or product in the following examples..arrow_forward(a) Which of the following phenols is the least acidic? (b) Which of the following phenols is the most acidic?arrow_forward(a) Draw the mechanism for the formation of both of the enols that can be formed from A (use acetic acid & AcOH as the source of the protons) (b) Draw the mechanism of reaction of this enol with bromine to give product Barrow_forward
- The saccharide shown here is present in some plant-derived foods. (a) Indicate the anomeric carbon atom(s) in this structure by drawing a circle around the atom(s) or by drawing an arrow pointing to the atom(s). (b) Would this saccharide give a positive result with Benedict’s reagent? Why or why not? (c) Would this saccharide give a positive result with Barfoed’s reagent? Why or why not? (d) Would this saccharide give a positive result with Seliwanoff’s reagent? Why or why not? (e) In a separate set of experiments, the saccharide solution was treated with a reagent that breaks glycosidic bonds. After this treatment, would any of the three assays give different results? Be sure to indicate which assay results would be different and give a reason.arrow_forwardConsider the following reaction scheme: (i) Provide the reagent(s) required for this transformation. (ii) Draw a curved arrow mechanism and comment on the stereoselectivity.arrow_forwardArrange the compounds in set in order of decreasing reactivity (fastest to slowest) toward electrophilic aromatic substitution.arrow_forward
- Give a clear handwritten answer with explanation...give the missing reagents for this reaction..complete the following reactionarrow_forwardResveratrol is an antioxidant found in the skin of red grapes. Its anticancer, anti-inammatory, and various cardiovascular effects are under active investigation. (a) Draw all resonance structures for the radical that results from homolysis of the OH bond shown in red. (b) Explain why homolysis of this OH bond is preferred to homolysis of either OH bond in the other benzene ring.arrow_forward(a) Draw two different halo ketones that can form A by an intramolecular alkylation reaction. (b) How can A be synthesized by an acetoacetic ester synthesis? of Aarrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





